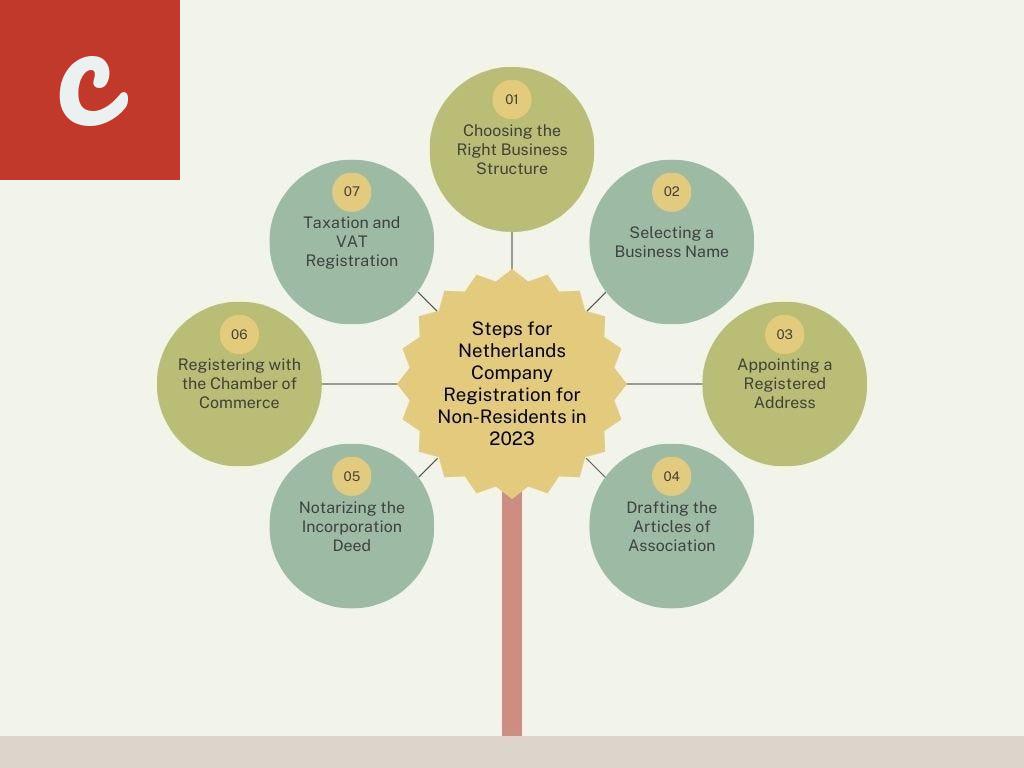
Understanding the Different Business Structures for Company Formation in the Netherlands
If you are considering starting a business in the Netherlands, it is essential to understand the different types of business structures available for company formation. Choosing the right structure is crucial, as it will impact various aspects of your business, including liability, taxes, and governance. Here are the main types of business structures in the Netherlands:
1. Sole Proprietorship:
A sole proprietorship is the simplest and most common form of business structure in the Netherlands. In this structure, the business is owned and operated by a single individual. As the sole proprietor, you have complete control over the business and are responsible for all its liabilities. However, keep in mind that your personal assets are not separate from the business, meaning you have unlimited liability. This structure is ideal for small businesses with low-risk activities.
2. Partnership:
A partnership is formed when two or more individuals come together to carry out a business with a shared purpose. There are two types of partnerships in the Netherlands: general partnerships (VOF) and limited partnerships (CV). In a general partnership, partners have equal rights and responsibilities and share profits and losses. In a limited partnership, there are two types of partners: general partners who bear unlimited liability and limited partners who have limited liability but do not actively participate in the management of the business. Partnerships are governed by a partnership agreement.
- General Partnership (VOF)
- Limited Partnership (CV)
3. Private Limited Liability Company (BV):
A private limited liability company, commonly known as a BV, is a legal entity separate from its shareholders. This means that the shareholders have limited liability, and their personal assets are protected from the company's debts. A BV requires a minimum starting capital of €0.01 and must have at least one shareholder and one director. BVs are subject to various legal and financial obligations, making them suitable for medium to large-sized businesses.
4. Public Limited Liability Company (NV):
A public limited liability company, known as NV, is similar to a BV with some differences. An NV can issue shares to the public, whereas a BV cannot. It also requires a higher minimum starting capital of €45,000. NNVs are subject to more stringent regulations, including the appointment of a supervisory board. This structure is typically used by larger companies that aim to raise capital through public offerings.
When choosing a business structure for your company formation in the Netherlands, it is crucial to consider factors such as liability, tax implications, administrative requirements, and the nature of your business activities. Consulting with a legal or tax professional can help you make an informed decision that best suits your needs and goals.
Selecting the Perfect Business Structure for Company Formation in the Netherlands
When it comes to company formation in the Netherlands, one crucial decision to make is selecting the right business structure. The choice of business structure will have a profound impact on your operations, legal obligations, tax liabilities, and overall success. Therefore, it is essential to understand the available options and choose the structure that best suits your needs.
The Netherlands offers several types of business structures, each with its own set of characteristics. Here are some of the most common business structures to consider:
- Sole Proprietorship: A sole proprietorship is the simplest form of business structure, where a single individual owns and operates the business. This structure offers minimal legal requirements and allows for easy decision-making. However, the owner is personally liable for all debts and legal obligations.
- Partnership: A partnership is formed when two or more individuals enter into a business together. This structure can be a general partnership (VOF) or a limited partnership (CV). In a general partnership, all partners are jointly and severally liable for the business's debts and obligations. In a limited partnership, there are general partners who have liability and limited partners who have limited liability.
- Private Limited Liability Company (BV): A BV is a separate legal entity that offers limited liability protection to its shareholders. This structure requires a minimum share capital of €0.01 and is the most popular choice for medium to large businesses in the Netherlands.
- Public Limited Liability Company (NV): An NV is similar to a BV but is suitable for larger companies with plans to go public in the future. It has more complex legal requirements, such as a minimum share capital of €45,000 and the need for a supervisory board.
- Branch Office: If you already have a company registered outside the Netherlands and wish to establish a presence in the country, setting up a branch office can be a suitable option. A branch office is not a separate legal entity and operates as an extension of the parent company.
When selecting the perfect business structure for your company formation in the Netherlands, several factors should be considered. These include the nature of your business, future growth plans, liability concerns, tax implications, and regulatory requirements.
To ensure you make the right decision, it is advisable to seek professional advice from a legal and tax expert familiar with Dutch company formations. They can guide you through the process, explain the pros and cons of each structure, and help you choose the one that aligns with your business goals.
In conclusion, selecting the right business structure for your company formation in the Netherlands is a critical step towards success. With careful consideration and professional guidance, you can choose a structure that provides the necessary legal protection, maximizes tax benefits, and supports your long-term business objectives. Take the time to evaluate your options and make an informed decision that will set the foundation for your business's growth and prosperity.
Main Title: Exploring the Best Business Structures for Setting Up a Company in the Netherlands
When it comes to setting up a company in the Netherlands, one of the first decisions entrepreneurs need to make is choosing the right business structure. The business structure you select can have a significant impact on your company's legal and financial aspects, as well as its growth potential. In this article, we will explore the best business structures for setting up a company in the Netherlands.
1. Sole Proprietorship:
A sole proprietorship is the simplest and most common business structure in the Netherlands. As the owner, you and your business are considered to be one entity, meaning you are personally liable for any business debts or obligations. This structure is ideal for small businesses, freelancers, and self-employed individuals who want full control over their operation.
- Advantages of Sole Proprietorship:
- Easy and inexpensive to set up.
- Complete control over the business.
- Minimal reporting requirements.
- Disadvantages of Sole Proprietorship:
- Unlimited personal liability.
- No separate legal entity.
- Difficult to raise capital.
2. Partnership:
A partnership in the Netherlands involves two or more individuals who share ownership and management responsibilities. There are two types of partnerships: general partnerships (VOF) and limited partnerships (CV). In a general partnership, all partners have equal rights and responsibilities, while in a limited partnership, there are general partners who manage the business and limited partners who have limited liability.
- Advantages of Partnership:
- Shared financial and managerial responsibilities.
- Flexible profit distribution.
- Easier access to capital.
- Disadvantages of Partnership:
- Unlimited personal liability in a general partnership.
- Partners are jointly liable for each other's actions.
- Difficult decision-making process.
3. Private Limited Company (BV):
A private limited company (BV) is the most popular business structure for entrepreneurs in the Netherlands. It offers limited liability to its shareholders, separate legal entity status, and flexibility in terms of shareholding and governance. The BV structure is suitable for medium to large-sized businesses or those seeking investments.
- Advantages of BV:
- Limited liability for shareholders.
- Separate legal entity.
- Easier access to funding and investments.
- Disadvantages of BV:
- Higher costs and administrative requirements.
- Tighter regulations and reporting obligations.
- Less control for individual shareholders.
4. Public Limited Company (NV):
A public limited company (NV) is similar to a BV in terms of limited liability and separate legal entity status. However, an NV is more suitable for larger businesses planning to go public or seeking external investors. It has stricter regulations and requires a minimum share capital.
- Advantages of NV:
- Limited liability for shareholders.
- Ability to issue shares to the public.
- Enhanced credibility for large-scale businesses.
- Disadvantages of NV:
- Higher share capital requirements.
- Strict regulations and reporting requirements.
- Complex decision-making process.
In conclusion, when starting a business in the Netherlands, carefully consider the different business structures available and choose the one that best suits your goals, needs, and circumstances. Consulting with legal and financial professionals can provide valuable insights to make an informed decision. Remember to bold keywords when optimizing your website content for better search engine rankings.
Main Title: The Pros and Cons of Different Business Structures for Company Formation in the Netherlands
Starting a business in the Netherlands can be a lucrative endeavor, but it's essential to choose the right business structure for your company formation. The business structure you choose will not only determine your legal obligations and financial liabilities but also impact your tax obligations, operational flexibility, and growth potential. In the Netherlands, there are several business structures to consider, each with its own pros and cons.
- Sole Proprietorship:
- Partnership:
- Private Limited Company (BV):
- Public Limited Company (NV):
A sole proprietorship is the simplest form of business structure in the Netherlands. This setup allows an individual to start and run a business as a sole owner. The main advantage of a sole proprietorship is its simplicity and low setup costs. You have complete control over decision-making, and the profits are yours to keep. However, as a sole proprietor, you are personally liable for all debts and legal obligations of your business.
If you're starting a business with one or more partners, a partnership structure might be suitable. There are two types of partnerships in the Netherlands: general partnership (VOF) and limited partnership (CV). In a general partnership, all partners share equal responsibility, liabilities, and profits. In a limited partnership, there are one or more general partners who are personally liable and one or more limited partners whose liability is limited to their investment.
A private limited company, also known as a BV, is a popular choice among entrepreneurs in the Netherlands. It offers limited liability to shareholders, meaning their personal assets are protected. A BV allows for multiple shareholders and can provide credibility and flexibility for growth. However, there are higher setup costs, ongoing administrative requirements, and more complex tax regulations compared to other business structures.
A public limited company, or NV, is suitable for larger businesses considering an initial public offering (IPO) or attracting external investors. It has more stringent requirements, including a minimum share capital of €45,000 and mandatory appointments of directors and a supervisory board. While an NV offers access to capital markets, it comes with increased reporting obligations and less flexibility in decision-making.
When selecting the right business structure for your company formation in the Netherlands, it's crucial to consider your long-term goals, financial capabilities, risk tolerance, and growth plans. Seeking advice from a legal professional or an experienced business consultant can help you make an informed decision and ensure compliance with Dutch regulations.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Business Structure for Company Formation in the Netherlands
When starting a business in the Netherlands, one of the most important decisions you will have to make is choosing the right business structure for your company. The business structure you select will determine various aspects of your business, including your legal obligations, tax liabilities, and the level of personal liability you will have as a business owner. To help you make an informed decision, here are some key factors to consider when choosing a business structure for company formation in the Netherlands:
- Legal Liability: One of the primary considerations when choosing a business structure is the level of legal liability you are comfortable with. Some structures, such as sole proprietorships and partnerships, offer less legal protection, making you personally liable for any debts or legal issues. On the other hand, limited liability structures like private limited companies (BV) and public limited companies (NV) provide more legal protection, limiting your personal liability to the amount you have invested in the business.
- Tax Implications: Another crucial factor to consider is the tax implications of the different business structures. Depending on the structure you choose, your business may be subject to different tax rates, deductions, and exemptions. For example, BVs are subject to corporate tax, while sole proprietorships and partnerships are subject to personal income tax. Consulting with a tax advisor can help you determine the most tax-efficient structure for your business.
- Ownership and Management: Consider your desired level of control and involvement in the business. Some structures, like sole proprietorships and partnerships, offer more autonomy and flexibility, allowing you to make decisions without consulting other shareholders. However, if you plan to raise capital from external investors or have a complex management structure with multiple shareholders, a BV or NV structure may be more suitable.
- Administrative Requirements: Different business structures come with varying administrative requirements. For instance, BVs and NVs have more stringent reporting and auditing requirements compared to sole proprietorships and partnerships. Consider the resources and time you are willing to invest in meeting these administrative obligations and choose a structure accordingly.
- Costs: Finally, take into account the setup and ongoing costs associated with each business structure. Some structures have higher initial setup costs and ongoing expenses, such as accountant fees and registration fees. Consider your budget and financial resources before deciding on a particular structure.
Choosing the right business structure is a critical decision that will impact various aspects of your business. Each structure has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it's important to carefully evaluate these key factors and consult with legal and tax professionals to ensure you make the best choice for your company formation in the Netherlands.



Comments on "Choosing The Right Business Structure For Company Formation In The Netherlands"
No comment found!