Main Title: A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing the Legal Structure for Company Formation in the Netherlands
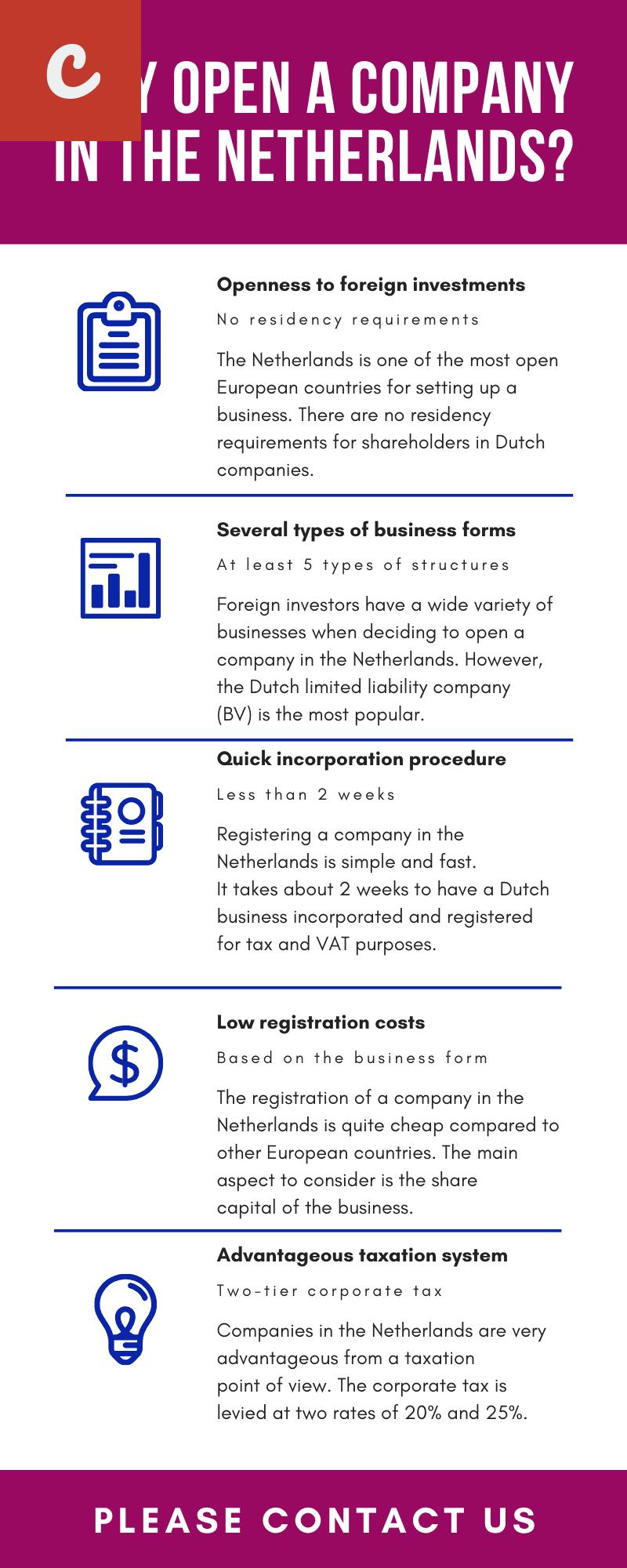
If you are considering starting a business in the Netherlands, one of the key decisions you need to make is choosing the legal structure for your company. The legal structure you choose will have implications for various aspects of your business, including taxation, liability, and decision-making processes. In this guide, we will provide you with an overview of the different legal structures available in the Netherlands, so you can make an informed decision.
1. Sole Proprietorship:
A sole proprietorship is the simplest form of legal structure in the Netherlands. As the name suggests, it is a business owned and operated by one person. As a sole proprietor, you have complete control over your business, but you also bear unlimited liability for any debts or obligations. This means that your personal assets could be at risk if your business encounters financial difficulties.
2. Partnership:
A partnership is a legal structure in which two or more individuals come together to run a business. There are two types of partnerships in the Netherlands: general partnership (VOF) and limited partnership (CV). In a general partnership, all partners are equally liable for the debts and obligations of the business. In a limited partnership, there are general partners who have unlimited liability and limited partners who have limited liability. The liability of limited partners is limited to their invested capital.
- Key points about partnerships:
- - Partners share profits and losses according to their share in the business;
- - Partnerships have their own legal status;
- - Partnerships are not subject to corporate income tax;
- - Partnerships are subject to personal income tax.
3. Private Limited Liability Company (BV):
A private limited liability company, or BV, is the most common legal structure for businesses in the Netherlands. As the name suggests, it offers limited liability protection to its shareholders. This means that the shareholders' personal assets are generally not at risk if the company encounters financial difficulties. The BV is a separate legal entity from its shareholders and requires a minimum share capital of 0.01 euro. A BV is subject to corporate income tax on its profits.
- Key points about BV:
- - Limited liability for shareholders;
- - Minimum share capital of 0.01 euro;
- - Subject to corporate income tax;
- - Obligation to publish annual financial statements.
4. Public Limited Liability Company (NV):
A public limited liability company, or NV, is a legal structure that is primarily used for larger businesses. It is similar to a BV but with additional requirements, such as a higher minimum share capital and the obligation to have a supervisory board. NVs are subject to corporate income tax and have additional obligations, such as publishing their annual financial statements.
In conclusion, choosing the right legal structure for your company formation in the Netherlands is an important decision that should not be taken lightly. Each legal structure has its own advantages and disadvantages, depending on your specific business needs and goals. Consulting with a legal or tax professional can help you make an informed decision and ensure compliance with Dutch laws and regulations.
Understanding the different legal structures for company formation in the Netherlands: A beginner's guide
Starting a business in the Netherlands can be an exciting endeavor. However, before diving into the entrepreneurial world, it is essential to understand the different legal structures available for company formation. Choosing the right legal structure is crucial as it determines the liability, tax obligations, and governance of your business.
Here, we will provide a comprehensive guide to help beginners navigate through the various legal structures in the Netherlands.
- Sole Proprietorship:
A sole proprietorship, or eenmanszaak in Dutch, is the simplest legal structure for starting a business. It is suitable for individuals running a small-scale operation on their own. As a sole proprietor, you are personally responsible for all business activities and liabilities. This means your personal assets may be at risk if the business encounters financial difficulties.
- Partnership:
A partnership structure, or vennootschap onder firma (VOF), is formed when two or more individuals decide to conduct business together. In a partnership, each partner contributes capital, shares profits, and is jointly liable for business debts. It is important to have a clear partnership agreement that outlines the responsibilities, profit-sharing, and exit strategies for each partner.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC):
A limited liability company, known as besloten vennootschap (BV) in the Netherlands, is a popular legal structure. It offers liability protection to its shareholders, who are only liable for the amount they have invested in the company. This structure allows for a clear separation between personal and business assets. BVs are subject to corporate tax and have a more complex administrative and reporting structure compared to sole proprietorships and partnerships.
- Public Limited Company (PLC):
A public limited company, or naamloze vennootschap (NV), is a legal structure suitable for large-scale businesses with publicly traded shares. This structure requires a minimum share capital of €45,000 and is subject to stricter regulations and reporting requirements. NVs are governed by a supervisory board and a management board. Shareholders' liability is limited to their share ownership.
It is crucial to consult with legal and tax professionals when choosing the right legal structure for your business. They can provide guidance tailored to your specific situation, ensuring compliance with Dutch laws and regulations.
Overall, understanding the different legal structures for company formation in the Netherlands is essential for a successful business launch. Whether you opt for a sole proprietorship, partnership, limited liability company, or public limited company, each structure has its benefits and considerations. Take the time to weigh the pros and cons, and select the legal structure that best suits your business goals.
Factors to Consider When Selecting the Appropriate Legal Structure for Company Formation in the Netherlands
When planning to start a business in the Netherlands, one crucial decision you need to make is choosing the appropriate legal structure for your company. This decision will have a significant impact on the way your business operates and the legal obligations you will have to fulfill. Therefore, it is important to consider several factors before finalizing your choice.
The first factor to consider is the extent of liability you are willing to bear. Different legal structures offer varying levels of liability protection. For instance, in a sole proprietorship or partnership, you will be personally liable for any debts or legal issues your business may face. On the other hand, if you opt for a limited liability company (LLC) or a public limited company (PLC), your liability will generally be limited to the amount of capital you invest in the company.
Secondly, you need to evaluate the taxation implications of each legal structure. The tax regime in the Netherlands varies depending on the legal form of your company. For instance, a sole proprietorship or partnership will require you to pay income tax on your profits, while an LLC or a PLC has separate corporate tax obligations. To determine the most tax-efficient structure for your business, it is recommended to consult with an accountant or tax advisor.
- Thirdly, the ease of formation and administration should be considered. Sole proprietorships and partnerships are relatively easy to set up and have fewer administrative requirements compared to LLCs and PLCs, which involve more complex procedures.
- Fourthly, consider the capital requirements of your business. A sole proprietorship or partnership does not have a minimum capital requirement, but an LLC or PLC usually does. If you have limited resources, a sole proprietorship or partnership may be more suitable.
Fifthly, analyze the level of control and decision-making you desire. In a sole proprietorship or partnership, you have complete control and decision-making power. Conversely, forming an LLC or a PLC means that you will have to share decision-making with other shareholders or directors.
Sixthly, consider the long-term goals and exit strategy for your business. If you plan to expand internationally or attract external investors, an LLC or PLC structure may be more advantageous. These legal forms provide more flexibility for growth and equity financing.
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate legal structure for your company formation in the Netherlands requires careful consideration of various factors. The extent of liability, taxation implications, ease of formation, capital requirements, level of control, and long-term goals should all be taken into account. By analyzing these factors and seeking professional advice, you can make an informed decision that suits the unique needs and objectives of your business.
Comparing legal structures for company formation in the Netherlands: Which one is right for you?
When it comes to starting a business in the Netherlands, one of the most important decisions is choosing the right legal structure for your company. There are several options available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
The most common legal forms for company formation in the Netherlands are:
- Sole proprietorship
- Private limited liability company (BV)
- Public limited liability company (NV)
- Cooperative
- Partnership
Sole proprietorship is the simplest and most straightforward legal structure. It is suitable for small businesses operated by a single individual. As a sole proprietor, you have full control over your business, but you are also personally liable for any debts or liabilities.
Private limited liability company (BV) is a popular choice for medium to large-sized businesses. It offers limited liability, meaning that the company's shareholders are not personally liable for its debts. BVs are highly flexible and can be easily transferred or sold.
Public limited liability company (NV) is similar to a BV, but with stricter regulations. It is usually reserved for larger companies planning to go public or seeking external financing. NVs have a more complex corporate governance structure and are subject to additional disclosure requirements.
Cooperative is a legal structure suitable for businesses with multiple owners or members. Cooperatives are often used by agricultural, financial, or social enterprises. Each member has an equal say in decision-making, and profits are distributed based on the members' contributions.
Partnership is formed when two or more individuals start a business together. Partnerships can be general partnerships (VOF) or limited partnerships (CV). In a general partnership, all partners are personally liable for the company's debts, while in a limited partnership, there are general partners who have unlimited liability and limited partners who have limited liability.
Choosing the right legal structure for your company depends on various factors, including your business goals, financial situation, and risk tolerance. Consulting with a legal professional or business advisor is recommended to ensure you make an informed decision.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between the legal structures for company formation in the Netherlands is crucial when starting a business. The choice between a sole proprietorship, BV, NV, cooperative, or partnership depends on your specific needs and circumstances. By carefully considering these options and seeking professional advice, you can make the right choice for your business.
Choosing the right legal structure is crucial for company formation in the Netherlands. It is essential to understand the various options available to ensure that your business operates smoothly and efficiently. In the Netherlands, one popular legal structure for company formation is the Dutch BV, or Besloten Vennootschap. A BV offers limited liability and enables the company to be a separate legal entity. If you are considering company formation in the Netherlands, it is essential to seek professional advice to guide you through the process. House of Companies is a reputable provider that offers comprehensive services for company formation in the Netherlands. Their expertise and guidance can help you navigate the complexities involved in establishing your business successfully. For more information, visit their website and learn about the benefits of forming a Dutch BV: Company Formation in The Netherlands.
Essential Tips for Deciding on the Ideal Legal Structure for Company Formation in the Netherlands
Are you thinking about starting a business in the Netherlands? One of the first and most important decisions you will need to make is choosing the ideal legal structure for your company formation. This decision will have long-term implications for your business, so it's crucial to choose wisely. Here are some essential tips to help you make the right choice:
1. Understand the Different Legal Structures: The Netherlands offers several legal structures for companies, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, limited liability companies (LLCs), and cooperatives. It's important to thoroughly understand the features, benefits, and limitations of each structure before making a decision.
2. Consider Liability Protection: Protecting your personal assets is a crucial consideration when choosing a legal structure. If you want to separate your personal and business liabilities, forming an LLC or a cooperative might be a wise choice.
3. Evaluate Tax Implications: Different legal structures have varying tax implications. It's essential to assess the tax obligations associated with each structure. Consulting with a tax advisor or an experienced company formation service provider can help you understand the tax implications and make an informed decision.
- 4. Cost and Administration: Consider the upfront costs and ongoing administrative requirements for each legal structure. Some structures may require more paperwork and higher costs for registration and compliance.
- 5. Future Growth and Funding: If you plan to expand your business and attract external investors in the future, it's essential to choose a legal structure that allows for such growth and facilitates fundraising activities.
6. Seek Professional Advice: Choosing the ideal legal structure for your company formation is a complex task. Engaging with a knowledgeable legal advisor or a company formation service provider can help you navigate the legal complexities, understand the implications, and make an informed decision.
Deciding on the ideal legal structure for your company formation in the Netherlands is a critical step towards establishing a successful business. By considering the tips mentioned above and seeking professional advice, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your business goals and aspirations.



Comments on "Choosing The Right Legal Structure For Company Formation In The Netherlands "
No comment found!