Understanding the Legal Requirements for Establishing a Company in the Netherlands
Establishing a company in the Netherlands can be an exciting endeavor. The Netherlands is known for its favorable business climate, skilled workforce, and strategic location within Europe. However, before diving into this venture, it is crucial to understand the legal requirements that accompany setting up a company in this country.
1. Choose the Right Business Structure
The first step in establishing a company in the Netherlands is to decide on the most suitable business structure. The options available include sole proprietorship, partnership, private limited liability company (BV), and public limited liability company (NV). Each structure has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it's important to thoroughly research and consult legal professionals to determine the best fit for your business.
- 2. Register your Business
Once you have selected the appropriate business structure, the next step is to register your company with the Dutch Chamber of Commerce (KVK). This registration is mandatory for all businesses operating in the Netherlands. During the registration process, you will need to provide information such as the company's name, address, business activities, and proof of identity for the company directors.
- 3. Obtain a Business Bank Account
In order to set up a company in the Netherlands, you will need to open a business bank account. This account will be used for the financial transactions of your company. The bank will require certain documents, such as your company's registration details, identification documents of the directors, and proof of address. It is advisable to contact banks in the Netherlands to compare their services and choose the most suitable option for your business needs.
- 4. Fulfill Tax Obligations
Another crucial aspect of establishing a company in the Netherlands is understanding and fulfilling your tax obligations. The Dutch tax system is complex, and it is important to familiarize yourself with the different taxes that your company may be subject to, such as corporate income tax, value-added tax (VAT), and payroll taxes. It is recommended to seek professional advice from a tax advisor or accountant to ensure compliance with the Dutch tax regulations.
- 5. Comply with Employment Laws
If your company plans to hire employees in the Netherlands, it is essential to comply with the country's employment laws. These laws cover areas such as minimum wage requirements, working hours, employment contracts, and employee benefits. Ensuring compliance with these regulations will help you avoid legal issues and maintain a positive working relationship with your employees.
In conclusion, establishing a company in the Netherlands comes with its own set of legal requirements. It is crucial to choose the right business structure, register with the Dutch Chamber of Commerce, open a business bank account, fulfill tax obligations, and comply with employment laws. Seeking professional advice and assistance will greatly facilitate the process and help you navigate the complexities of Dutch corporate law. By understanding and fulfilling these requirements, you can set up a successful and legally compliant business in the Netherlands.
A Comprehensive Guide to Setting Up a Company in the Netherlands: Legal Requirements
If you are considering starting a company in the Netherlands, understanding the legal requirements is vital. The Netherlands offers a favorable business climate and various opportunities for entrepreneurs. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the legal requirements to set up a company in the Netherlands.
1. Choosing the Right Legal Structure
The first step in setting up a company in the Netherlands is choosing the right legal structure. Common options include Sole Proprietorship, Private Limited Company (BV), Public Limited Company (NV), and Partnership. Each legal structure has its advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to consider factors such as liability, taxation, and ownership.
- Sole Proprietorship: Suitable for small businesses owned by a single person. The owner is personally liable for all debts and obligations of the business.
- Private Limited Company (BV): The most common legal structure. Shareholders have limited liability, and there is a separation between personal and company assets.
- Public Limited Company (NV): Suitable for larger companies with multiple shareholders. It allows the company to raise capital through the sale of shares on the stock market.
- Partnership: Suitable for businesses with two or more owners. There are various types of partnerships, including general partnership (VOF) and limited partnership (CV).
2. Company Registration
Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your company with the Dutch Chamber of Commerce (Kamer van Koophandel or KvK). Registration involves providing information about the company, such as its name, address, activities, and legal structure. You will also need to appoint a director, who will be responsible for the day-to-day management of the company.
3. Business Banking
Opening a business bank account is a requirement for setting up a company in the Netherlands. Choose a reputable bank and provide the necessary documentation, including your company registration details and identification. A business bank account will allow you to receive payments, pay expenses, and keep clear financial records.
4. Tax Registration
All businesses in the Netherlands must register for taxation purposes. You will need to obtain a tax identification number (TIN) from the Dutch Tax and Customs Administration (Belastingdienst). Depending on the nature of your business, you may have additional tax obligations, such as VAT (Value Added Tax) registration or payroll taxes.
5. Employer Obligations
If you plan to hire employees for your company, you have certain employer obligations to fulfill. This includes registering as an employer with the Dutch Tax and Customs Administration, providing payroll administration, and adhering to labor laws and regulations. It's important to familiarize yourself with the legal requirements for employing staff in the Netherlands.
Setting up a company in the Netherlands can be an exciting venture. By understanding and fulfilling the legal requirements, you can establish a solid foundation for your business. Consider seeking professional advice from a Dutch lawyer or business advisor to ensure compliance with all legal obligations.
Starting a Business in the Netherlands: Navigating the Legal Requirements
Are you planning to start a business in the Netherlands? This beautiful country, known for its vibrant business culture and strong economy, offers numerous opportunities for entrepreneurs. However, before diving into this exciting venture, it is essential to understand the legal requirements involved in starting a business in the Netherlands.
1. Legal Structure:
The first step is to decide on the legal structure of your business. The most common options in the Netherlands are sole proprietorship, partnership, and limited liability company (LLC). Each structure has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it's crucial to choose the one that best suits your needs.
- Sole Proprietorship: This is the simplest and most flexible form of business ownership. As a sole proprietor, you will be personally liable for any debts or obligations of your business.
- Partnership: A partnership is suitable if you plan to start a business with one or more partners. Each partner will share responsibilities, profits, and losses.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): An LLC offers limited liability protection, separating your personal and business assets. It requires more administrative work and higher costs but provides a higher level of protection.
2. Business Registration:
Once you have chosen a legal structure, you need to register your business with the Dutch Chamber of Commerce (Kamer van Koophandel or KvK). Registration allows you to obtain a unique identification number, known as a KVK number, which is necessary for various legal and administrative purposes.
3. Taxation:
Understanding the tax system in the Netherlands is crucial for any business owner. The main taxes you need to consider are corporate income tax, value-added tax (VAT), and payroll taxes. Hiring an experienced tax advisor can help ensure that you comply with all tax obligations and take advantage of beneficial tax structures.
4. Permits and Licenses:
Depending on the nature of your business, you may need specific permits or licenses to operate legally in the Netherlands. Some businesses, such as restaurants or childcare facilities, require additional certifications or health and safety permits. Research the specific requirements for your industry and seek guidance from the relevant authorities or industry associations.
5. Contracts and Agreements:
When starting a business, you will likely enter into several contracts and agreements. It is essential to have well-drafted contracts in place to protect your interests and clearly define your rights and obligations. Consult a legal professional to ensure that your contracts comply with Dutch laws and regulations.
Conclusion:
Starting a business in the Netherlands can be a rewarding endeavor, but it is vital to navigate the legal requirements properly. Understanding the different legal structures, registering your business, complying with tax obligations, obtaining necessary permits and licenses, and having well-drafted contracts are key steps to successfully establish your business in the Netherlands. Seeking professional advice where necessary will help you ensure compliance and protect your business interests.
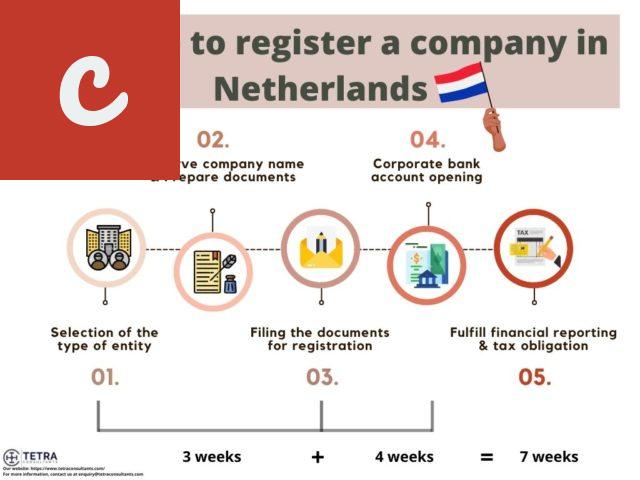
Main Title: Key Legal Obligations for Establishing a Company in the Netherlands
When considering establishing a company in the Netherlands, it is important to understand the key legal obligations that you must adhere to. By being aware of these obligations, you can ensure that you are in compliance with the law and avoid any potential legal issues.
One of the first legal obligations you will encounter is the need to register your company with the Dutch Chamber of Commerce (Kamer van Koophandel, or KvK). This registration is mandatory and must be completed within one week of starting your business activities. By doing so, you will receive a KvK number, which is crucial for various administrative purposes.
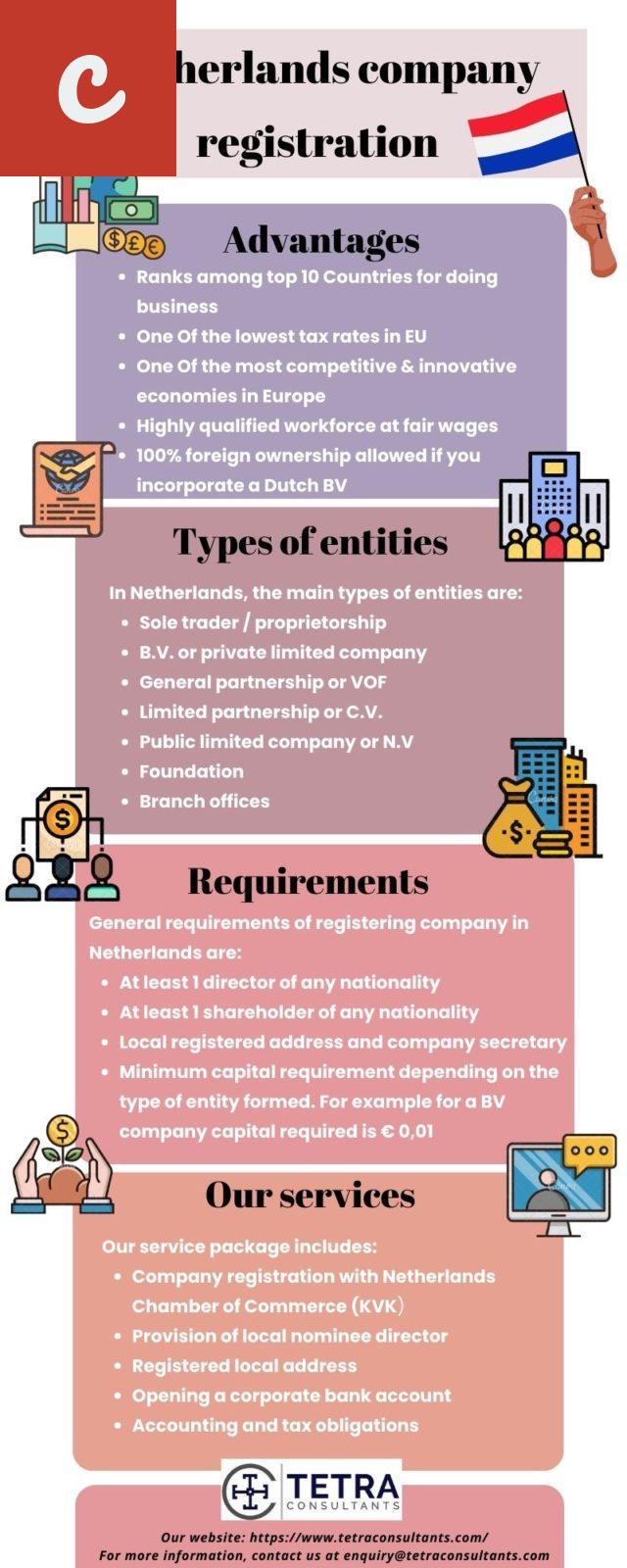
Another important obligation is the choice of legal structure for your company. In the Netherlands, you can establish different types of legal entities, such as a sole proprietorship (eenmanszaak), a partnership (maatschap or vennootschap onder firma), or a limited liability company (besloten vennootschap, or BV). Each structure has its own legal requirements and implications, so it is essential to carefully consider which one best suits your needs.
- List item 1: If you choose to establish a BV, you will need to draft and notarize articles of association and appoint at least one director. Additionally, you will be required to deposit a minimum share capital of €0.01.
- List item 2: For a partnership or sole proprietorship, you will need to register with the KvK and may also need to fulfill certain other requirements, such as obtaining specific licenses or permits depending on your business activities.
Furthermore, it is essential to comply with the relevant tax obligations. This includes registering for tax purposes with the Dutch Tax and Customs Administration (Belastingdienst) and ensuring timely submission of tax returns. The specific tax obligations will depend on the legal structure of your company and the nature of your business.
Additionally, companies in the Netherlands are subject to various employment and labor laws. This includes obligations related to minimum wages, employee contracts, and workplace safety. It is vital to familiarize yourself with these regulations to ensure that you are providing fair and safe working conditions for your employees.
Lastly, maintaining accurate and up-to-date financial records is crucial. Dutch law requires companies to keep proper accounting records and file annual financial statements with the Chamber of Commerce. In some cases, companies may need to have their financial statements audited by a certified auditor.
In conclusion, establishing a company in the Netherlands comes with several legal obligations. By registering with the KvK, choosing the appropriate legal structure, fulfilling tax obligations, complying with employment laws, and maintaining accurate financial records, you can ensure that your business operates in accordance with Dutch law. It is advisable to seek legal and professional advice to ensure full compliance and avoid any legal pitfalls.
Main Title: The Essential Legal Requirements for Setting Up a Company in the Netherlands
Setting up a company in the Netherlands can be an exciting endeavor. However, it's important to understand the legal requirements involved to ensure a smooth and successful establishment of your business. Here are the essential legal steps you need to take:
1. Choose the Legal Structure: The first step in setting up a company in the Netherlands is to determine the legal structure. The most common options are a sole proprietorship, partnership, or a private limited company (BV).
2. Register at the Trade Register: To legally operate a company in the Netherlands, you need to register your business with the Trade Register of the Chamber of Commerce. This registration provides you with a unique registration number, which is essential for various legal and administrative purposes.
- List item 1: Submit the registration documents to the Chamber of Commerce, including identification, proof of address, and the chosen legal structure of your business.
- List item 2: Pay the registration fees, which depend on the legal structure and services you require.
3. Obtain a VAT Number (BTW-Nummer): If your company is engaged in taxable business activities, you need to obtain a VAT number. This number is required for invoicing, tax reporting, and compliance with VAT regulations.
4. Register for Taxes: Depending on your activities, you may need to register for other taxes, such as corporate income tax, payroll tax, or social security contributions. Ensure compliance with tax regulations to avoid penalties in the future.
5. Business Insurance: It's advisable to consider business insurance to protect your company from potential liabilities. Although it's not legally required, it can provide financial security and peace of mind.
6. Employment Contracts and Labor Laws: If you plan to hire employees, you must comply with Dutch labor laws. This includes providing written employment contracts, complying with minimum wage and working hour regulations, and adhering to health and safety requirements.
7. Intellectual Property Protection: If your business involves intellectual property, such as inventions, trademarks, or copyrights, it's essential to protect your rights. Registering your intellectual property can safeguard your unique assets and prevent unauthorized use.
Setting up a company in the Netherlands involves several legal steps and requirements. It's recommended to seek professional advice or consult a legal expert to ensure compliance with all the necessary regulations. Taking the time to understand and fulfill these legal obligations will set a strong foundation for your business success in the Netherlands.



Comments on "Legal Requirements For Setting Up A Company In The Netherlands"
No comment found!