Understanding Taxation and Accounting Regulations for Company Formation in the Netherlands
When it comes to company formation in the Netherlands, understanding the taxation and accounting regulations is crucial. The Netherlands is known for its business-friendly environment and favorable tax policies, making it an attractive destination for entrepreneurs and investors.
Taxes
The Dutch taxation system consists of various taxes that companies need to be aware of. The main taxes include corporate income tax, value-added tax (VAT), payroll taxes, and dividend tax.
Corporate Income Tax: All companies incorporated in the Netherlands are subject to corporate income tax. The standard corporate income tax rate is 25%. However, there is a reduced rate of 15% applicable to the first €245,000 of profits for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Value-Added Tax (VAT): VAT is applicable to most goods and services provided in the Netherlands. The standard VAT rate is 21%, with reduced rates of 6% and 0% applicable to certain goods and services. Companies need to register for VAT and keep proper records for filing VAT returns.
Payroll Taxes: If your company has employees, you will need to deduct and remit payroll taxes from their salaries. These taxes include income tax, employee insurance contributions, and social security contributions. It is important to comply with the Dutch employment laws and regulations when it comes to payroll taxes.
Dividend Tax: The Netherlands has a dividend tax, which is a tax on profits distributed to shareholders. The tax rate is currently set at 15%. However, in certain cases, exemptions or reduced rates may apply depending on tax treaties with other countries.
Accounting Regulations
Companies in the Netherlands are required to follow specific accounting regulations. The Netherlands has adopted the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) for financial reporting. This means that companies need to prepare their financial statements in accordance with IFRS guidelines.
Depending on the size of your company, different reporting standards may apply. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can also follow the Dutch generally accepted accounting principles (Dutch GAAP) instead of IFRS, providing some flexibility in reporting requirements.
- Meeting annual reporting requirements is essential to comply with Dutch regulations.
- Audit requirements exist for larger companies, which must have their financial statements audited by a registered auditor.
Conclusion
Understanding taxation and accounting regulations is vital for successfully establishing and operating a company in the Netherlands. By familiarizing yourself with the Dutch tax system and accounting requirements, you can ensure compliance and effectively manage your company's financial affairs. Seeking professional advice from tax advisors and accountants can greatly assist in navigating the complex regulations and optimizing tax strategies for your business.
Understanding Taxation and Accounting Regulations for Company Formation in the Netherlands
The Netherlands has long been a popular destination for entrepreneurs and businesses looking to expand their operations in Europe. With its stable economy, favorable business climate, and strategic location, it offers numerous opportunities for both local and foreign entrepreneurs. However, before setting up your company in the Netherlands, it is essential to understand the taxation and accounting regulations that govern the process.
Taxation Regulations
When it comes to taxation, the Netherlands has a comprehensive regime that applies to both individuals and companies. All businesses in the country are subject to various taxes, including corporate tax, value-added tax (VAT), payroll tax, and dividend tax.
The corporate tax rate in the Netherlands is currently set at 25%. However, for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), there is a lower tax rate of 15% on the first €245,000 of taxable profit. It is worth noting that the Netherlands has an extensive network of tax treaties with many countries, which can provide opportunities for tax optimization and avoidance of double taxation.
Value-added tax, commonly known as VAT, is applicable to most goods and services in the Netherlands. The standard VAT rate is 21%, but reduced rates of 9% and 0% apply to specific goods and services. It is crucial to be aware of the VAT obligations and regulations to ensure compliance and avoid any potential penalties or fines.
Accounting Regulations
Compliance with accounting regulations is crucial for all companies in the Netherlands. As per the Dutch Commercial Code, companies are required to prepare annual financial statements, including a balance sheet, income statement, and explanatory notes. The financial statements must comply with the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) in the Netherlands.
In addition to preparing financial statements, companies must also appoint an auditor to conduct an annual audit. The audit is mandatory for large and medium-sized companies, while small companies may be exempt under certain circumstances.
- List Item 1: Familiarize yourself with the Dutch tax and accounting system
- List Item 2: Seek professional advice and expertise
Taking the Right Steps
When it comes to company formation in the Netherlands, navigating taxation and accounting regulations can be complex. Therefore, it is essential to take the right steps and seek professional guidance to ensure compliance and optimize your tax position.
By familiarizing yourself with the Dutch tax and accounting system, you can better understand the requirements and obligations that come with running a business in the country. Seek advice from reputable tax and accounting professionals who specialize in company formation to ensure that you receive accurate and up-to-date information.
In conclusion, understanding taxation and accounting regulations is vital for anyone planning to form a company in the Netherlands. Compliance with these regulations is not only essential for legal and financial reasons but also for the long-term success of your business.
Essential Tips for Complying with Taxation and Accounting Regulations when Forming a Company in the Netherlands
Forming a company in the Netherlands offers numerous advantages for entrepreneurs looking to establish a business in Europe. With its stable economy, strategic location, and favorable tax regime, the Netherlands has become an attractive destination for foreign investors. However, like any other country, the Netherlands has certain taxation and accounting regulations that need to be complied with. Here are some essential tips to ensure that you meet these obligations when forming a company in the Netherlands:
1. Understand the Dutch Tax System
Before establishing your business in the Netherlands, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with the Dutch tax system. The tax regime in the Netherlands is complex, comprising various taxes such as corporate income tax, value-added tax (VAT), payroll tax, and dividend tax. Consulting with a tax advisor or accountant who specializes in Dutch taxation can help you navigate through the system efficiently.
2. Keep Accurate Financial Records
One of the key requirements when forming a company in the Netherlands is to maintain accurate financial records. This includes keeping track of all income, expenses, and transactions related to your business. By maintaining proper financial records, you will be able to fulfill your accounting obligations and easily prepare financial statements required by Dutch authorities.
3. Hire a Qualified Accountant
Hiring a qualified accountant is essential to ensure compliance with Dutch accounting standards. An experienced accountant can help you manage your bookkeeping, prepare financial statements, and file the necessary tax returns. They can also provide guidance on tax planning strategies to optimize your tax position within the boundaries of the law.
- 4. Register for Taxes
- 5. Stay Up-to-Date with Tax Law Changes
When forming a company in the Netherlands, you need to register for various taxes, such as VAT, payroll tax, and corporate income tax. Registering for these taxes is a crucial step to fulfill your tax obligations. Depending on the size and nature of your business, you may also need to register with other regulatory bodies, such as the Dutch Chamber of Commerce.
Tax laws and regulations in the Netherlands are subject to change. It is essential to stay informed about any amendments or updates to tax laws that may impact your business. Regularly consulting with a tax advisor or accountant can help you adapt to these changes and ensure that you remain compliant.
Complying with taxation and accounting regulations when forming a company in the Netherlands is crucial for avoiding penalties and maintaining good standing with the authorities. By understanding the Dutch tax system, keeping accurate financial records, hiring a qualified accountant, registering for taxes, and staying up-to-date with tax law changes, you can establish and operate your business in the Netherlands smoothly and efficiently.
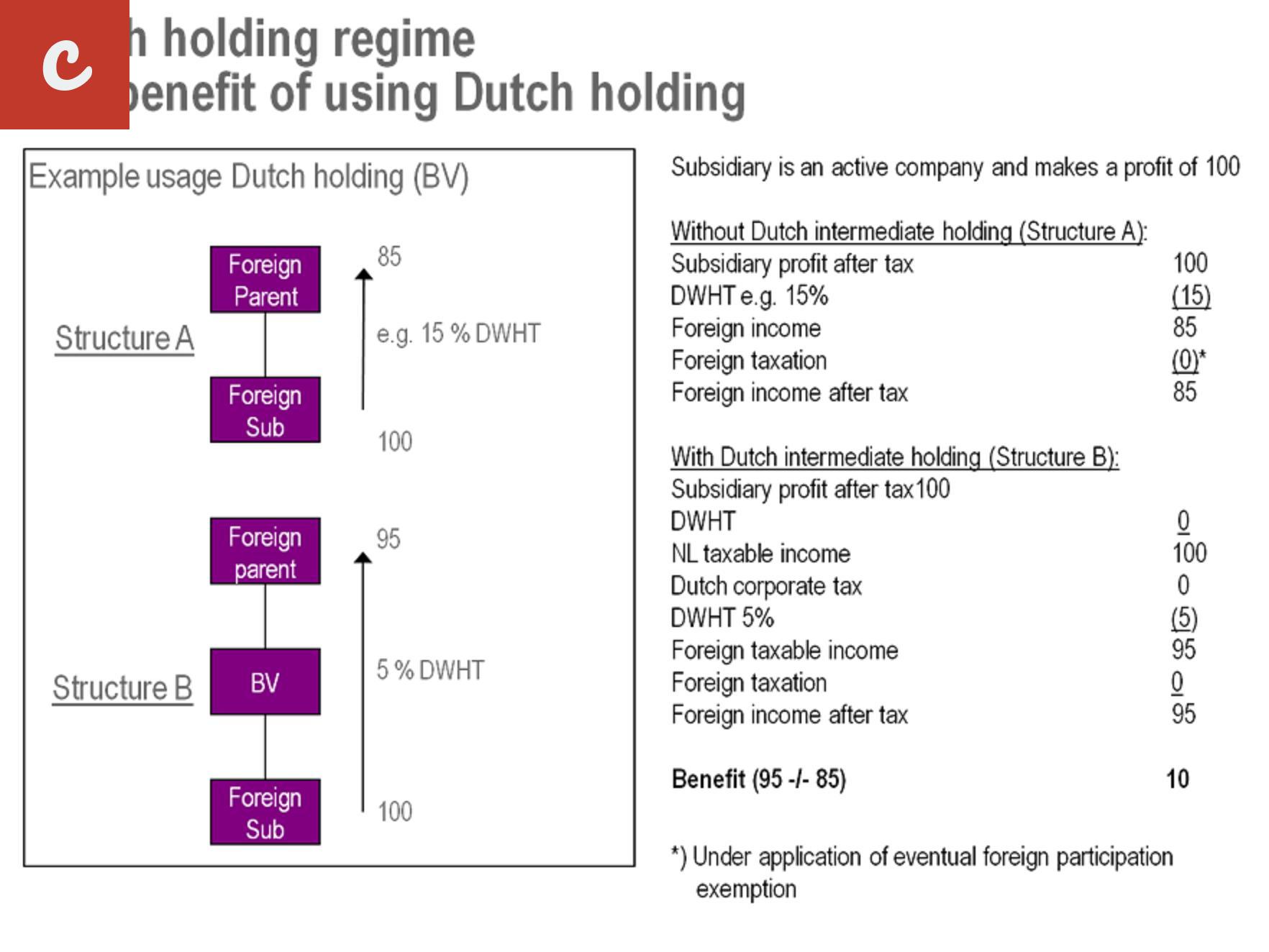
Key Considerations for Managing Taxation and Accounting Regulations during Company Formation in the Netherlands
When it comes to expanding your business internationally, the Netherlands is often seen as an attractive destination due to its favorable tax climate, strategic location, and open economy. However, it is crucial to understand the taxation and accounting regulations in the country to ensure smooth company formation and operation.
Taxation Regulations
The first step in managing taxation during company formation is to understand the different tax regimes in the Netherlands. The main types of taxes that businesses need to be aware of are corporate income tax, value-added tax (VAT), and payroll tax.
- Corporate Income Tax: Companies in the Netherlands are subject to corporate income tax on their worldwide profits. The standard corporate income tax rate is 25%, applicable to profits up to €200,000. For profits exceeding this threshold, a higher tax rate of 21.7% is applicable.
- Value-Added Tax (VAT): VAT is levied on the supply of goods and services in the Netherlands. There are different VAT rates depending on the nature of the goods or services. Standard rate is 21%, reduced rate is 9%, and a zero rate applies to certain goods and services.
Accounting Regulations
Compliance with accounting regulations is essential for businesses in the Netherlands. The Dutch Civil Code requires companies to prepare annual financial statements in accordance with the Dutch Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) for larger companies. Small and medium-sized enterprises can also prepare financial statements in accordance with the Dutch GAAP if they meet specific criteria.
It is important to note that companies in the Netherlands are required to file their financial statements with the Dutch Chamber of Commerce. Non-compliance with accounting regulations can result in penalties and legal consequences.
Other Considerations
In addition to taxation and accounting regulations, there are other important considerations to keep in mind during company formation in the Netherlands:
- Legal Structure: Choosing the right legal structure for your company, such as a private limited liability company (BV) or a branch office, is crucial as it impacts taxation, liability, and governance.
- Tax Planning: Working with a tax advisor or accountant is advisable to develop an effective tax planning strategy, minimize tax liabilities, and take advantage of available tax incentives and exemptions.
Conclusion
Managing taxation and accounting regulations is an integral part of company formation in the Netherlands. Understanding the tax regimes, complying with accounting regulations, and considering other relevant aspects are key to establishing and operating a successful business in the country. Seeking the guidance of a professional tax advisor or accountant can help navigate the complexities and ensure compliance with all regulations.
Navigating Taxation and Accounting Regulations: What You Need to Know for Company Formation in the Netherlands
Starting a company in the Netherlands can be an exciting and rewarding venture. However, it's essential to understand the taxation and accounting regulations for a smooth and successful company formation process. This article will outline the key things you need to know to navigate these regulations effectively.
Taxation
One of the critical aspects of company formation is understanding the Dutch taxation system. The Netherlands has a transparent and business-friendly tax regime, making it an attractive destination for entrepreneurs. Here are some essential taxation elements you should be aware of:
- Corporate Income Tax: Companies in the Netherlands are subject to corporate income tax on their worldwide profits. The basic tax rate is 25%, applicable to profits up to €200,000. For profits exceeding this threshold, the rate is reduced to 15%.
- VAT: Value Added Tax (VAT) is applicable to most goods and services provided or sold in the Netherlands. The standard VAT rate is 21%, with reduced rates of 9% and 0% applying to specific products and services.
- Employer Payroll Taxes: When you hire employees, you will need to pay employer payroll taxes, which include social security contributions, healthcare contributions, and wage tax.
Accounting Regulations
Compliance with accounting regulations is vital for any company operating in the Netherlands. Here are some key points to consider:
- Financial Statements: Companies are required to prepare annual financial statements following generally accepted accounting principles. These include a balance sheet, profit and loss statement, and notes to the financial statements.
- Accounting Records: It is essential to maintain accurate and up-to-date accounting records. These records must be kept for a period of at least seven years and be available for inspection by tax authorities.
- Audit Requirements: Companies may be subject to annual audits, depending on their size and the number of employees. Smaller companies with total assets below €6,000,000 and less than 50 employees may be exempt from this requirement.
Seek Professional Advice
Given the complex nature of taxation and accounting regulations, it is highly recommended to seek professional advice when setting up a company in the Netherlands. Consulting with a tax advisor, accountant, or legal expert can ensure compliance with all requirements and help you optimize your tax position.
In conclusion, understanding the taxation and accounting regulations is crucial when starting a company in the Netherlands. Familiarize yourself with corporate income tax, VAT, and employer payroll taxes to meet your tax obligations. Furthermore, comply with accounting regulations to prepare accurate financial statements and maintain proper accounting records. By seeking professional advice, you can navigate these regulations seamlessly and focus on growing your business.




Comments on "Navigating Taxation And Accounting Regulations For Company Formation In The Netherlands"
No comment found!