Demystifying Taxation Laws for Company Formation in the Netherlands
Establishing a company in the Netherlands can be an attractive option for entrepreneurs around the world. With its favorable business climate, strategic location, and strong infrastructure, the Netherlands offers excellent opportunities for growth and expansion. However, before embarking on the journey of company formation in the Netherlands, it is crucial to understand the taxation laws to ensure compliance and maximize profitability.
The Dutch taxation system is known for its transparency and simplicity. The country offers various tax benefits and incentives that make it an attractive destination for businesses. One of the key aspects to consider is the corporate income tax (CIT) rate, which currently stands at 25%. However, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can benefit from a reduced CIT rate of 15% on the first €245,000 of profits. This reduced rate encourages entrepreneurship and supports the growth of SMEs in the country. It is important to mention that these rates are subject to change, so it is advisable to consult tax professionals or the Dutch Tax and Customs Administration for up-to-date information.
- Deductible Expenses: Dutch tax laws allow businesses to deduct various expenses, such as rent, salaries, and business-related costs. It is important to maintain detailed records and receipts to support these deductions and ensure compliance with the tax regulations. Deductible expenses can help reduce the overall tax liability of the company and increase profitability.
- VAT Registration: Value Added Tax (VAT) is an essential aspect of company formation in the Netherlands. Businesses with an annual turnover exceeding €20,000 must register for VAT. The standard VAT rate in the Netherlands is 21%, but reduced rates of 9% and 0% apply to specific goods and services. VAT returns must be filed periodically, and it is recommended to seek guidance from tax professionals to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with VAT regulations.
Moreover, the Netherlands has an extensive tax treaty network, allowing businesses to benefit from reduced withholding tax rates on cross-border payments. This network eliminates double taxation and provides a platform for businesses to expand globally while minimizing tax liabilities.
When setting up a company in the Netherlands, it is essential to determine its legal structure, as different forms have different tax implications. The most common types of legal entities in the Netherlands are sole proprietorships, partnerships, and private limited companies (BV). Each legal structure has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of taxation, liability, and regulatory requirements. It is advisable to consult legal and tax experts to choose the most suitable legal structure based on individual circumstances and business goals.
To summarize, understanding the taxation laws for company formation in the Netherlands is crucial for entrepreneurs looking to establish their presence in this business-friendly country. It is recommended to seek professional advice to navigate the complexities of the tax system, maximize tax incentives, and ensure compliance with Dutch tax regulations. With the right knowledge and guidance, businesses can leverage the transparent and lucrative tax environment in the Netherlands to thrive and succeed.
Understanding Taxation Laws for Company Formation in the Netherlands
Setting up a company in the Netherlands can be a smart move for entrepreneurs due to its strategic location, business-friendly environment, and favorable taxation laws. However, before diving into the process of company formation, it is important to have a clear understanding of the taxation laws that apply to businesses in the Netherlands.
One key aspect to consider is the corporate income tax. In the Netherlands, companies are subject to a standard corporate income tax rate of 25% on their worldwide profits. However, there is a reduced rate of 15% for the first €200,000 of profits, known as the innovation box. This incentives companies that invest in research and development, making the Netherlands an attractive destination for innovative businesses.
Another important tax to be aware of is the value-added tax (VAT). In the Netherlands, most goods and services are subject to VAT at a standard rate of 21%. However, there are also reduced rates of 9% and 0% that apply to specific goods and services, such as food, books, and medicine. Understanding the VAT system is crucial for businesses to correctly calculate and report their VAT obligations.
- Income tax for employees:
- Social security contributions:
In addition to corporate taxes, employee income is subject to personal income tax in the Netherlands. The income tax rates are progressive, ranging from 9.45% to 49.5% depending on the level of income. Employers are also responsible for deducting the appropriate amount of income tax from their employees' salaries and remitting it to the tax authorities.
Both employers and employees are required to make contributions to social security in the Netherlands. The contribution rates are based on the employee's earnings, with the employer typically responsible for paying the majority of the contribution. These contributions help fund healthcare, pensions, and other social welfare benefits.
Additionally, the Netherlands has an extensive network of tax treaties with other countries to avoid double taxation. These treaties ensure that income earned by Dutch companies abroad is not taxed both in the foreign country and in the Netherlands. It is important to consult with tax professionals to take advantage of these treaties and optimize your tax position.
When starting a business in the Netherlands, complying with taxation laws is vital for long-term success and avoiding any legal issues. It is highly recommended to seek professional advice from accountants or tax advisors with expertise in international taxation and Dutch regulations.
In conclusion, the Netherlands provides a favorable tax environment for company formation. Understanding and navigating through the taxation laws, such as corporate income tax, VAT, income tax for employees, social security contributions, and tax treaties is crucial for entrepreneurs looking to establish a successful business in the Netherlands.
Understanding the Complexities of Taxation Laws for Company Formation in the Netherlands
When it comes to setting up a company in the Netherlands, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the taxation laws that govern business operations. The Dutch tax system is known for its complexities and can be daunting to navigate without the right expertise. This article aims to shed light on the intricacies of taxation laws for company formation in the Netherlands.
The first step in starting a business in the Netherlands is choosing the appropriate legal structure. The most common forms of business entities are a private limited company (BV) and a sole proprietorship (eenmanszaak). Each structure has its own tax implications, and understanding them is crucial for making an informed decision.
- List item 1: For a BV, the tax rate is 15% for taxable profits up to €200,000 and 25% for profits exceeding this threshold. Furthermore, dividends distributed by the BV are subject to a 15% withholding tax.
- List item 2: On the other hand, a sole proprietorship's income is taxed under the income tax regime. The tax rates depend on the income bracket and can range from 9.7% to 49.5%.
Another crucial aspect of the Dutch tax system is the Value Added Tax (VAT), known as Omzetbelasting (OB). Companies engaging in taxable activities are required to charge VAT on their goods or services. The standard VAT rate in the Netherlands is 21%, while a reduced rate of 9% applies to specific goods and services, such as food and medical products.
In addition to corporate and value-added taxes, the Netherlands has implemented various other tax regulations that affect businesses. These include the payroll tax, dividend tax, and environmental taxes, among others. It is essential to understand these regulations and ensure compliance to avoid legal complications.
When starting a business in the Netherlands, it is highly recommended to seek the guidance of a professional tax advisor or accountant with expertise in Dutch taxation laws. They can help navigate the complexities of the tax system, ensure compliance, and optimize tax planning strategies.
In conclusion, understanding the taxation laws for company formation in the Netherlands is crucial for any entrepreneur looking to start a business in the country. The intricacies of the Dutch tax system can be challenging, but with the right professional expertise, businesses can successfully navigate through the complexities and optimize their tax planning strategies for long-term success.
Essential Tips for Navigating Taxation Laws during Company Formation in the Netherlands
Starting a company in the Netherlands can be an exciting and rewarding venture. With its favorable business climate and robust economy, the Netherlands has become a popular destination for entrepreneurs and foreign investors. However, navigating taxation laws during company formation can be a complex process. To ensure compliance and avoid any potential issues, here are some essential tips to consider:
Understand the Dutch Tax System: Before starting your business in the Netherlands, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with the Dutch tax system. The tax laws and regulations can vary depending on the type of business entity you choose. Research and consult with tax professionals to understand the different tax implications for each business structure.
Consult with Tax Professionals: Taxation laws can be intricate, especially for foreign entrepreneurs. It is advisable to seek the guidance of tax professionals who are well-versed in Dutch tax legislation. They can provide advice tailored to your specific situation, ensuring compliance with tax obligations and helping you optimize your tax strategy.
- Register with the Dutch Tax Authorities: As a company operating in the Netherlands, you must register with the Dutch Tax Authorities. This includes obtaining a tax identification number and registering for VAT (Value Added Tax), if applicable. Ensure that you complete the necessary paperwork and meet all the registration requirements.
- Research Tax Incentives: The Dutch government offers various tax incentives to encourage entrepreneurship and stimulate investment. These incentives can significantly benefit your business by reducing the tax burden. Explore the available tax breaks and subsidies, such as the Innovation Box regime or the Research and Development tax credit, to see if your company qualifies.
Maintain Accurate Financial Records: Proper bookkeeping and record-keeping are essential for compliance with Dutch tax laws. Establish a robust accounting system to accurately track all financial transactions. Ensure that you retain all relevant documents, such as invoices and receipts, to substantiate your tax deductions and claims.
Stay Updated with Tax Changes: Tax laws are subject to change, and it is essential to stay informed and updated on any modifications that may affect your company's tax obligations. Regularly review tax updates and consult with tax professionals to ensure compliance with the latest regulations.
File Tax Returns on Time: Meeting tax deadlines is crucial to avoid penalties and negative consequences. In the Netherlands, companies are required to file various tax returns, including corporate income tax, VAT, and payroll tax. Ensure you understand the filing requirements and deadlines for each tax type and submit your returns on time.
In conclusion, navigating taxation laws during company formation in the Netherlands requires proper understanding, planning, and compliance. By following these essential tips and seeking professional guidance, you can ensure that your business operates smoothly within the Dutch tax system. Remember, it's always recommended to consult tax professionals who can provide personalized advice based on your unique circumstances.
Main Title: Mastering Taxation Laws for Successful Company Formation in the Netherlands
Taxation laws play a crucial role in the process of company formation in the Netherlands. Understanding and mastering these laws is essential for the successful establishment of a company in this European powerhouse. In this article, we will explore the key taxation laws that every entrepreneur should be familiar with when planning to start a company in the Netherlands.
The first and foremost taxation law to consider is the corporate income tax. This tax is levied on the profits generated by the company. In the Netherlands, the corporate income tax rate is currently set at 25%. It is important to note that this rate is subject to change, so it is advisable to consult with a tax advisor or professional before making any financial decisions.
Additionally, the Netherlands offers various tax incentives and deductions to encourage business growth and innovation. One such incentive is the Research and Development (R&D) tax credit. Companies engaged in R&D activities may be eligible for a tax credit that reduces their tax liability. This credit can be a significant advantage for companies investing in research and development.
Another important aspect of taxation laws in the Netherlands is the Value Added Tax (VAT). VAT is levied on goods and services provided by businesses. The standard VAT rate in the Netherlands is 21%, but reduced rates of 9% and 0% are applicable to specific goods and services. It is crucial for entrepreneurs to understand the VAT regulations and compliance requirements to avoid any penalties or legal issues.
- List item 1: The Netherlands also has a favorable tax treaty network with various countries, which is beneficial for international businesses. These treaties aim to avoid double taxation and provide tax advantages to businesses with cross-border activities.
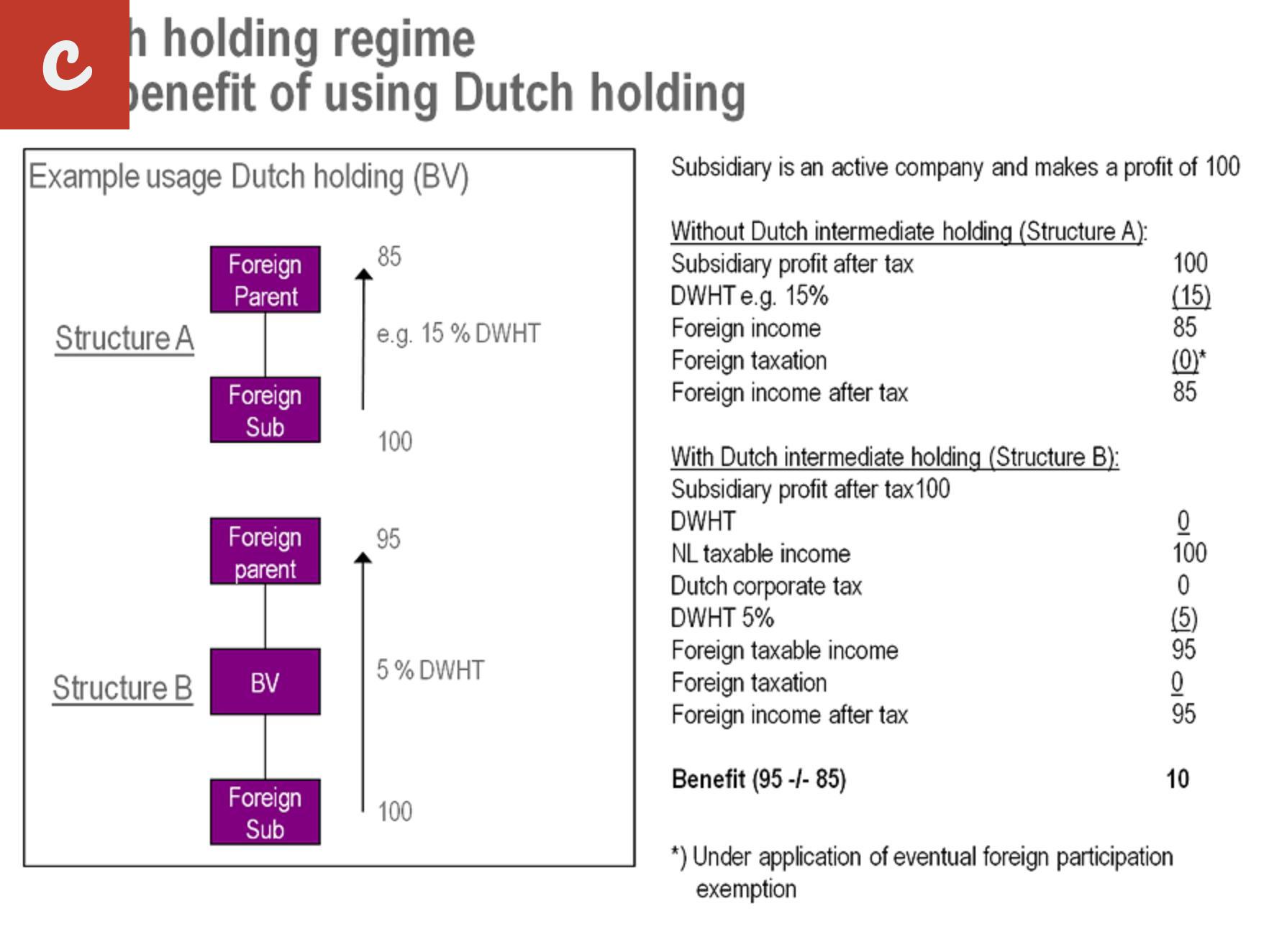
- List item 2: Moreover, the Netherlands offers an attractive tax climate for holding companies. A holding company is a company that primarily holds shares in other companies. The Dutch tax system provides exemptions for certain dividend income and capital gains, making it an attractive jurisdiction for holding companies.
Lastly, it is crucial to note that taxation laws are subject to frequent changes and updates. Staying updated with the latest tax regulations and amendments is essential for compliance and maximizing tax efficiency. Seeking professional advice from tax experts or consultants can provide invaluable guidance in navigating the complexities of taxation laws in the Netherlands.
In conclusion, mastering taxation laws is essential for successful company formation in the Netherlands. Familiarizing yourself with key laws such as corporate income tax, VAT, tax incentives, and the favorable tax treaty network will help you establish and operate your business efficiently. Remember to stay updated with the latest tax regulations and consult with professionals to ensure compliance and optimize tax planning strategies.




Comments on "Navigating Taxation Laws For Company Formation In The Netherlands"
No comment found!