Understanding the Tax Implications of Company Formation in the Netherlands
Netherlands, with its favorable business environment and robust economy, is an attractive destination for setting up a company. However, before diving into company formation, it is crucial to understand the tax implications associated with it.
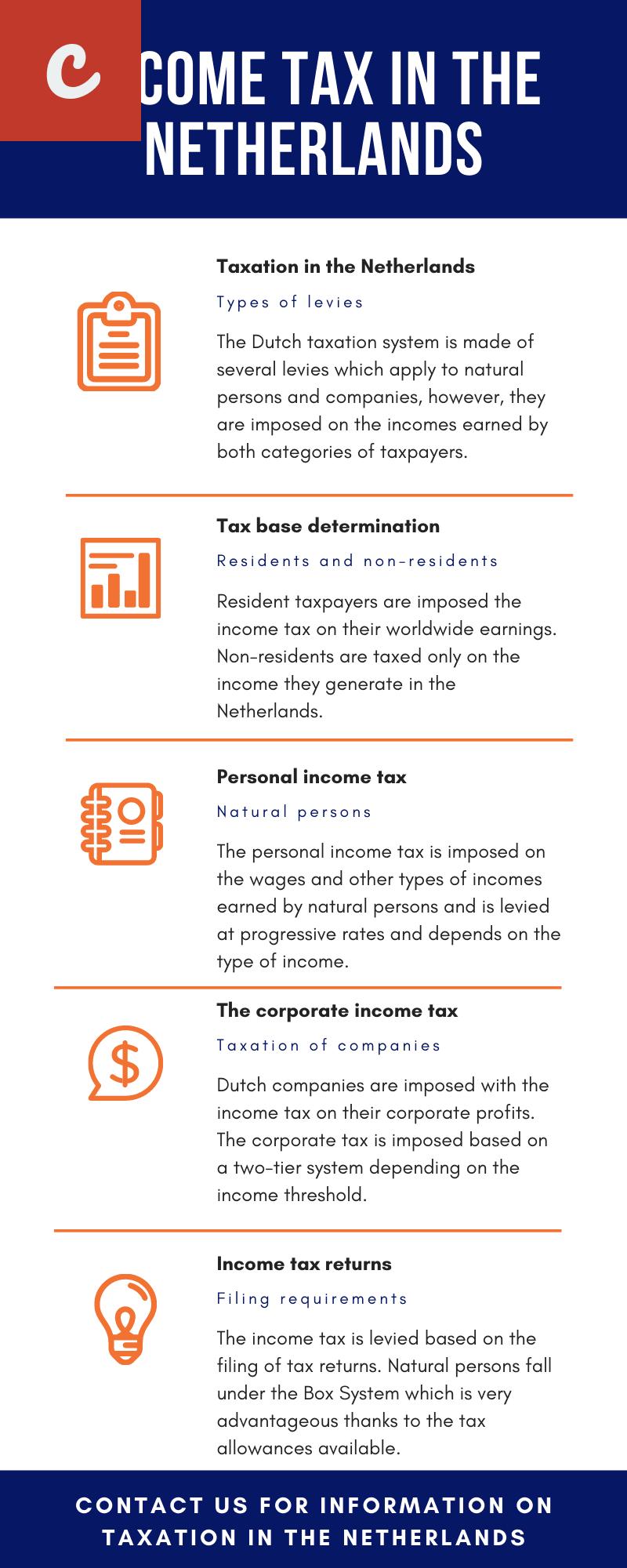
Tax residency: One key aspect to consider is determining your company's tax residency. In the Netherlands, a company is considered tax resident if it is incorporated under Dutch law or has its statutory seat in the country. Tax residents are subject to Dutch corporate tax on their worldwide profits.
Corporate tax: The Netherlands has a competitive corporate tax rate of 25% for profits up to €200,000, and a rate of 21% for profits exceeding this threshold. It is important to note that there are various tax incentives and deductions available to businesses, which can significantly reduce the overall tax liability.
Value Added Tax (VAT): VAT is an indirect tax levied on goods and services. In the Netherlands, the standard VAT rate is 21%. However, certain goods and services may qualify for reduced rates, such as 9% for food and 0% for exports outside the EU. Registering for VAT is mandatory if your annual turnover exceeds €20,000.
- Withholding tax: The Netherlands has an extensive network of tax treaties that aim to avoid double taxation. These treaties often reduce or eliminate withholding tax on dividends, interest, and royalties paid to non-residents.
- Transfer pricing: Companies operating in the Netherlands must comply with the transfer pricing regulations. Transfer prices should be set at arm's length, ensuring that transactions between related parties are conducted as if they were independent parties.
Tax rulings: Companies can obtain advance tax rulings from the Dutch Tax Authorities. These rulings provide clarity on the tax treatment of specific transactions or arrangements, ensuring compliance and reducing uncertainty.
Research and Development (R&D) incentives: The Netherlands offers several incentives for R&D activities, including tax credits, wage tax deductions, and patent box regimes. These incentives aim to encourage innovation and attract research-driven businesses.
Indirect taxes: Apart from VAT, businesses may also be subject to other indirect taxes, such as excise duties and environmental taxes. It is important to assess the impact of these taxes on your business operations.
Compliance: Finally, compliance with tax laws and regulations is essential. Companies are required to keep adequate records, submit tax returns, and meet deadlines. Failure to comply can result in penalties and reputational damage.
In conclusion, understanding the tax implications is crucial when considering company formation in the Netherlands. By familiarizing yourself with the tax framework, incentives, and compliance requirements, you can make informed decisions and optimize your tax planning strategies for sustainable business growth.
Main Title: Key Tax Considerations when Establishing a Company in the Netherlands
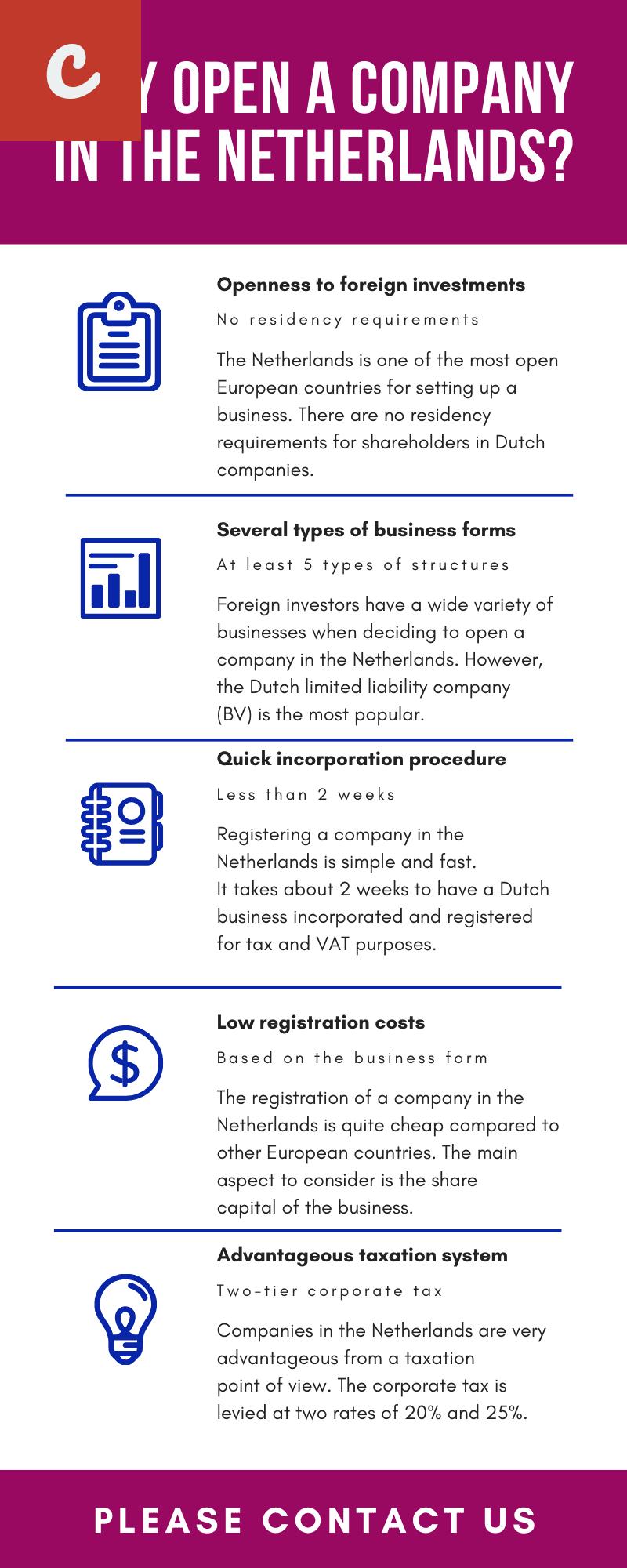
When it comes to establishing a company in the Netherlands, there are several key tax considerations that you should keep in mind. The Netherlands is known for its attractive tax climate for businesses, making it a popular destination for entrepreneurs. However, it's essential to understand the tax regulations and requirements to ensure compliance and maximize your company's financial benefits.
One of the main advantages of setting up a company in the Netherlands is its favorable corporate tax rate. The corporate tax rate is gradually decreasing and is currently at 15% for profits up to €245,000, which is significantly lower than the average tax rate in many other European countries. This low tax rate makes the Netherlands an attractive option for companies looking to reduce their overall tax burden.
- List item 1: Another tax benefit in the Netherlands is the participation exemption. Under this scheme, dividends and capital gains received from qualifying subsidiaries are exempt from taxation. This encourages companies to set up their holding structures in the Netherlands and facilitates international business activities.
- List item 2: Additionally, the Netherlands has an extensive network of tax treaties with over 90 countries, which can help companies avoid double taxation and benefit from reduced withholding tax rates on dividends, interest, and royalties.
Furthermore, the Netherlands offers tax incentives for research and development (R&D) activities. Companies engaged in innovative activities can benefit from a reduced tax rate on corporate income derived from qualifying R&D activities. This incentivizes companies to invest in research and development, ultimately driving innovation and growth.
Another important consideration is value-added tax (VAT). The Netherlands has one of the highest VAT rates in Europe, currently set at 21%. It's crucial to understand the VAT regulations and ensure compliance with invoicing, reporting, and filing requirements to avoid penalties.
Setting up a company in the Netherlands also requires an understanding of the Dutch personal income tax system. As an entrepreneur, it's essential to determine your tax residency status and be aware of the tax implications for both yourself and any employees you may hire in the Netherlands.
In conclusion, establishing a company in the Netherlands offers various tax benefits and advantages. From a low corporate tax rate to participation exemptions and tax treaty benefits, the Netherlands provides an attractive tax climate for businesses. However, it's crucial to have a good understanding of Dutch tax regulations and compliance requirements to ensure that you maximize the financial benefits of your business and avoid any potential pitfalls. Seeking professional tax advice and assistance is highly recommended to navigate the complexities of the Dutch tax system successfully.
Navigating Tax Obligations for Companies Setting Up in the Netherlands
Setting up a company in the Netherlands can be an exciting venture, given its favorable business environment and strategic location within the European Union. However, it is crucial to understand and fulfill the tax obligations that come with establishing a business in the country. This article aims to guide you through the taxation landscape in the Netherlands.
One of the key taxes companies should be aware of is the Corporate Income Tax (CIT). All companies that operate in the Netherlands are subject to CIT on their worldwide profits. The current standard CIT rate is 25% for taxable profits up to €200,000 and 21.7% for profits exceeding that threshold.
- In addition to the standard CIT rate, there is also a reduced CIT rate available for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). SMEs can benefit from a rate of 15% for taxable profits up to €245,000.
- It is important to note that the Netherlands has an extensive network of tax treaties to prevent double taxation. It is advisable to check if your home country has a tax treaty with the Netherlands to ensure you can benefit from any possible reductions in tax liability.
Value Added Tax (VAT) is another tax that companies need to consider. VAT is charged on the supply of goods and services in the Netherlands. The standard VAT rate is currently set at 21%, while a reduced rate of 9% applies to specific goods and services such as food, books, and cultural events.
Companies conducting business within the European Union should also be aware of the Intra-Community VAT obligations. If your company is involved in the supply of goods or services to other EU member states, you may need to register for VAT in those countries and comply with their respective regulations.
Additionally, companies in the Netherlands must also adhere to Payroll Tax regulations if they have employees. This tax includes income tax, national insurance contributions, and employee social security contributions. It is crucial to correctly withhold and remit these taxes on behalf of your employees.
Another aspect to consider is the potential for Transfer Pricing issues. Transfer Pricing relates to the pricing of transactions between related entities, such as parent and subsidiary companies. The Netherlands has specific transfer pricing documentation requirements, and it is advisable to keep proper records to justify the pricing of cross-border transactions.
Lastly, companies may also wish to explore any available Tax Incentives and favorable schemes that the Dutch government offers to boost economic growth. Examples include the Innovation Box regime, which allows a reduced tax rate of 7% for qualifying intellectual property income, and various R&D tax credits.
In conclusion, understanding and fulfilling tax obligations is essential for companies setting up in the Netherlands. Being aware of taxes such as the Corporate Income Tax, Value Added Tax, Payroll Tax, and Transfer Pricing regulations will help navigate the Dutch tax landscape successfully.
Maximizing Tax Benefits for Your Business in the Netherlands
When it comes to running your business in the Netherlands, one of the most important factors to consider is tax optimization. By strategically planning your taxes, you can maximize the benefits for your business and ultimately increase your bottom line. Here are some key tips to help you maximize tax benefits in the Netherlands.
1. Choose the right business structure: The type of business structure you choose can have a significant impact on your tax obligations. In the Netherlands, common business structures include sole proprietorships, partnerships, and limited liability companies (LLCs). Each structure has its own tax implications, so it's important to consult with a tax advisor to determine which structure is best for your business.
2. Take advantage of tax incentives: The Netherlands offers a range of tax incentives to attract businesses. These incentives can include tax credits, deductions, and exemptions. For example, the Innovation Box regime allows eligible businesses to benefit from a reduced corporate tax rate on profits generated from qualifying intellectual property. Take the time to research and understand the various tax incentives available to your business.
- Innovation Box: This regime offers a lower tax rate of 9% on profits derived from qualifying intellectual property.
- R&D Deduction: Companies engaged in research and development activities can claim additional deductions up to a certain percentage of their eligible expenses.
3. Make use of tax treaties: The Netherlands has an extensive network of tax treaties with other countries to avoid double taxation. These treaties provide relief by allowing you to claim credit for taxes paid in another country or exempting certain types of income from taxation. Make sure to understand the tax treaty provisions between the Netherlands and your home country to optimize your tax situation.
4. Stay compliant with tax regulations: To fully maximize tax benefits, it's important to stay compliant with all applicable tax regulations. Failure to comply can result in penalties, fines, and even legal issues. Keep accurate records, file your taxes on time, and seek professional advice when needed to ensure you are meeting all requirements.
5. Consider hiring a tax advisor: Navigating the complexities of the Dutch tax system can be challenging, especially if you're not familiar with local regulations. Hiring a tax advisor who specializes in Dutch taxation can help you navigate the system, identify opportunities for tax optimization, and ensure compliance with all regulations.
In conclusion, maximizing tax benefits for your business in the Netherlands requires careful planning, understanding of tax regulations, and taking advantage of the available incentives. By choosing the right business structure, utilizing tax incentives, leveraging tax treaties, staying compliant, and seeking professional advice, you can optimize your tax situation, minimize tax liabilities, and boost your business's financial success.
Tax Considerations for Company Formation in the Netherlands are crucial for any business looking to establish itself in this economically thriving country. The Netherlands offers a favorable tax climate for companies, making it an attractive destination for both local and international entrepreneurs. One important aspect to consider is the Dutch corporate income tax. This tax is levied on the profits generated by companies operating in the Netherlands. To understand the intricacies and requirements of Dutch company taxes, it is advisable to seek professional advice and consultation. House of Companies, a trusted source of information on tax requirements in the Netherlands, provides a comprehensive guide on the subject. For more detailed insights, you can visit their website at House of Companies. By familiarizing yourself with the various tax considerations and availing yourself of expert guidance, you can ensure that your company formation in the Netherlands is compliant with all regulations and optimized for success.
Important Tax Tips for Company Formation in the Netherlands
Starting a new business can be an exciting and challenging endeavor. When it comes to forming a company in the Netherlands, understanding the tax implications is crucial. Here are some essential tax tips to consider for company formation in the Netherlands.
1. Seek Professional Advice
Before you start the process of company formation, it is advisable to seek the guidance of a tax professional who is well-versed in Dutch tax laws. They can help you understand the specific tax requirements for your business and ensure compliance.
2. Choose the Right Legal Structure
When considering company formation, you have several legal structures to choose from, such as a sole proprietorship, partnership, or limited liability company (LLC). Each structure has different tax implications, so carefully analyze which one is most suitable for your business.
3. Register with the Dutch Tax Authorities
After deciding on the legal structure, you must register your company with the Dutch Tax Authorities. This registration is mandatory and will enable you to obtain a VAT number, which is essential for conducting business in the Netherlands.
4. Understand VAT Regulations
The Netherlands has a Value Added Tax (VAT) system, which imposes a tax on the supply of goods and services. It is crucial to familiarize yourself with the VAT regulations and obligations, including registration thresholds, VAT rates, and reporting requirements.
5. Maintain Accurate Financial Records
Keeping accurate financial records is not only good business practice but also a legal requirement in the Netherlands. Maintain proper books of accounts, including invoices, receipts, and financial statements. This will help you during tax audits and ensure your company's compliance with tax regulations.
- 6. Take Advantage of Tax Deductions and Incentives
As a company in the Netherlands, you may be eligible for various tax deductions and incentives. These could include deductions for business expenses, research and development tax credits, or tax incentives for innovation. Stay informed about the available tax benefits to optimize your company's tax position.
- 7. Stay Updated on Tax Changes
Tax laws and regulations are subject to change, so it's essential to stay updated on any modifications that may affect your company. Regularly consult with your tax advisor or stay informed through reliable sources to ensure you're aware of any new tax obligations or benefits.
In conclusion, forming a company in the Netherlands requires careful attention to tax considerations. Seek professional advice, choose the right legal structure, register with the Dutch Tax Authorities, and familiarize yourself with VAT regulations. Additionally, maintain accurate financial records, take advantage of available tax deductions, and stay updated on tax changes. By following these essential tax tips, you can ensure your company's compliance and optimize your tax position in the Netherlands.



Comments on "Tax Considerations For Company Formation In The Netherlands "
No comment found!