Understanding the Tax Implications of Company Formation in the Netherlands
When starting a business, one of the key considerations is the tax implications that come with company formation. If you are considering starting a company in the Netherlands, it is important to understand the tax regulations and requirements in order to properly plan and manage your financial obligations.
The first step is to familiarize yourself with the different types of companies that can be formed in the Netherlands. The most common types are limited liability companies (BV) and sole proprietorships (Eenmanszaak). Each of these company structures has its own tax implications, so it is important to choose the one that aligns with your business goals and financial situation.
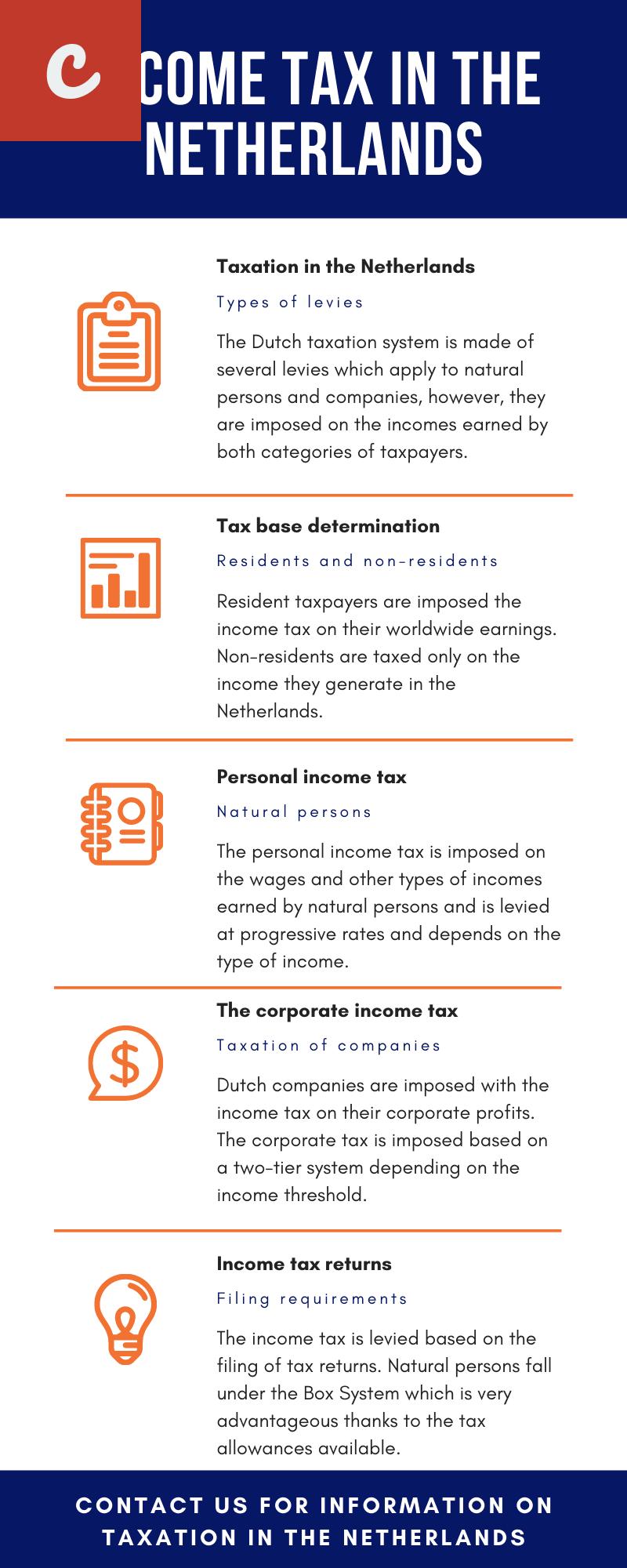
A limited liability company (BV) is a separate legal entity from its owners. It offers limited liability protection, meaning that the owners' personal assets are not at risk if the company incurs debts. This type of company is subject to corporate tax on its profits. The current corporate tax rate in the Netherlands is 25% for profits up to €200,000 and 21.7% for profits exceeding €200,000.
On the other hand, a sole proprietorship (Eenmanszaak) is not a separate legal entity. The owner is personally liable for all the debts and obligations of the business. In this case, the owner reports the business income on their personal income tax return, which is subject to progressive income tax rates ranging from 9.7% to 49.5%.
- Company Formation Requirements
- Once you have decided on the type of company structure, there are certain requirements that need to be met for company formation in the Netherlands.
- These include:
- Registering with the Dutch Commercial Register
- Obtaining a tax identification number (RSIN)
- Appointing a legal representative (if necessary)
- Opening a business bank account
It is also crucial to understand the value-added tax (VAT) system in the Netherlands. As a business owner, you may be required to charge and collect VAT on your products or services. The current standard VAT rate in the Netherlands is 21%, although there are reduced rates of 9% and 0% for specific goods and services.
Tax benefits and incentives
The Netherlands offers several tax benefits and incentives to promote business growth and investment. One example is the Innovation Box regime, which allows eligible companies to apply a reduced corporate tax rate of 9% on profits derived from qualifying intellectual property (IP) assets.
Furthermore, the Netherlands has double taxation agreements with many countries, which can help to avoid or reduce the taxation of income earned internationally. These agreements ensure that income is not taxed twice, both in the country where it is earned and in the country of residency.
Conclusion
Understanding the tax implications of company formation in the Netherlands is vital for any business owner. By choosing the right company structure and ensuring compliance with tax regulations, you can effectively manage your tax obligations and take advantage of the available tax benefits and incentives. Consulting with a tax professional can provide further guidance and assistance in navigating the complexities of the Dutch tax system.
Key Tax Factors to Consider When Setting up a Company in the Netherlands
Setting up a company in the Netherlands can be an exciting opportunity, but it is important to understand the key tax factors associated with starting a business in this country. Here are some important considerations to keep in mind:
Corporate Income Tax:
The corporate income tax rate in the Netherlands is 25%. However, there is a reduced rate of 15% for taxable profits up to €200,000. It is important to consider the tax implications of your business income and structure your company accordingly.
Value Added Tax (VAT):
VAT is an important tax consideration for businesses operating in the Netherlands. The standard VAT rate is 21%, but there are reduced rates of 9% and 0% for certain goods and services. It is crucial to understand the VAT rules and obligations to ensure compliance and avoid any penalties.
Wage Tax and Social Security Contributions:
When hiring employees in the Netherlands, you will be responsible for deducting and remitting wage tax and social security contributions. The wage tax rates vary depending on the income level, and both the employer and employee contribute to social security. Understanding these obligations is crucial to properly manage your payroll.
Transfer Pricing:
If your company operates internationally and has transactions with related entities, it is important to consider transfer pricing rules. The Netherlands has transfer pricing rules based on the OECD guidelines to prevent improper shifting of profits. Proper documentation is necessary to support your transfer pricing arrangements.
Research and Development (R&D) Incentives:
The Netherlands offers attractive incentives for companies engaged in research and development activities. These incentives include the Innovation Box, which allows for a reduced corporate income tax rate of 7% on qualifying profits derived from innovative activities. It is important to understand these incentives and determine if your business qualifies.
- Tax planning and compliance:
- When setting up a company in the Netherlands, it is essential to engage with tax advisors who can provide guidance on tax planning and compliance. They can help you navigate the complexities of the Dutch tax system and ensure that you meet all your tax obligations.
In conclusion, when setting up a company in the Netherlands, it is crucial to consider the key tax factors that will impact your business. Understanding corporate income tax, VAT, wage tax, transfer pricing, R&D incentives, and engaging with tax advisors will help you stay compliant and optimize your tax situation. Take the time to properly plan and structure your business to maximize your success in the Netherlands.
Understanding Tax Regulations for Company Formation in the Netherlands
When it comes to starting a business in the Netherlands, it is crucial to have a good grasp of the tax regulations in place. The Netherlands is known for its business-friendly environment and attractive tax system, making it an ideal destination for entrepreneurs. However, to ensure a smooth company formation process and avoid any potential tax-related issues, it is essential to understand the tax regulations that apply.
1. Corporate Income Tax (CIT)
The Netherlands has a relatively low corporate income tax rate compared to many other European countries. As of 2021, the standard corporate income tax rate is 25%. However, there is a lower rate of 15% applicable to the first €245,000 of taxable profits for qualifying small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
2. Value Added Tax (VAT)
VAT is an important tax to consider for businesses operating in the Netherlands. The standard VAT rate is currently 21%, which applies to most products and services. However, reduced VAT rates of 9% and 0% are also applicable to specific goods and services, such as food, books, and healthcare.
- List item 1: If your company's turnover exceeds €20,000 per year, you are required to register for VAT in the Netherlands.
- List item 2: Once registered, you will need to file regular VAT returns and pay any VAT due to the tax authorities.
3. Payroll Taxes
If you plan to hire employees in the Netherlands, it is important to be aware of the payroll tax obligations. The payroll taxes consist of income tax, social security contributions, and wage tax. You, as the employer, are responsible for deducting and remitting these taxes to the Dutch tax authorities.
4. Personal Income Tax
If you are planning to reside in the Netherlands while operating your business, it is crucial to understand the personal income tax regulations. The Netherlands operates a progressive tax system, with rates ranging from 9.7% to 49.5%, depending on your income level.
In some cases, entrepreneurs may qualify for the so-called "30% ruling," which allows for a tax-free reimbursement of certain expenses. This ruling applies to expatriate employees and entrepreneurs coming to the Netherlands for work.
Overall, navigating tax regulations for company formation in the Netherlands requires careful attention to detail and understanding of the applicable rules. Consulting with a tax advisor or hiring a professional can help ensure compliance and optimize your tax situation. By familiarizing yourself with the tax regulations mentioned above, you can start your business in the Netherlands with confidence and minimize any tax-related complications.

Tax Planning Tips for Establishing a Business in the Netherlands
Are you considering establishing a business in the Netherlands? It's important to understand the tax implications and plan accordingly. The Netherlands offers an attractive tax environment for businesses, with various incentives and benefits. Here are some tax planning tips to keep in mind:
- Choose the right legal structure: The first step in tax planning is selecting the appropriate legal structure for your business. The Netherlands offers several options, including sole proprietorship, partnership, and limited liability company. Each structure has its own tax benefits and requirements, so consult with a tax advisor to determine the best choice for your business.
- Take advantage of tax incentives: The Dutch government has implemented various tax incentives to encourage entrepreneurship and innovation. For example, the Innovation Box offers a reduced corporate tax rate of 9% on income derived from qualifying intellectual property. Additionally, the Dutch government provides generous tax deductions for research and development activities.
Investigate tax treaties: The Netherlands has an extensive network of tax treaties with other countries to prevent double taxation. These treaties can help reduce your tax burden by allowing you to claim tax credits or exemptions on income earned abroad. Familiarize yourself with the tax treaties between the Netherlands and your home country to optimize your tax planning strategy.
Utilize the participation exemption: The participation exemption is a key tax advantage for businesses in the Netherlands. It allows companies to receive dividends and capital gains from qualifying subsidiaries tax-free. To benefit from this exemption, certain criteria must be met, such as having a substantial ownership interest in the subsidiary. Consult with a tax advisor to ensure you meet the necessary requirements.
Consider VAT registration: If your business generates an annual turnover exceeding a certain threshold, you may be required to register for Value Added Tax (VAT). VAT is levied on goods and services provided by businesses and is typically collected from consumers. By registering for VAT, you can deduct the VAT you pay on business expenses from the VAT you collect on sales, resulting in a lower overall tax liability.
Obtain personalized advice: Tax planning can be complex, especially when establishing a business in a foreign country. It's crucial to seek personalized advice from a tax professional who specializes in Dutch taxation. They can help you navigate the intricacies of the tax system, identify additional tax planning opportunities, and ensure compliance with all relevant regulations.
In conclusion, tax planning is a vital aspect of establishing a business in the Netherlands. By understanding the tax implications and utilizing the available incentives, you can optimize your tax position and reduce your tax liability. Remember to consult with a tax advisor to develop a tailored tax planning strategy that aligns with your business goals and objectives.
Tax considerations for company formation in the Netherlands are crucial for businesses seeking to establish a presence in this European country. The Dutch corporate income tax is an important aspect of these considerations. It is essential to thoroughly understand the tax requirements imposed on Dutch companies to ensure compliance and optimal financial planning. To learn more about the tax requirements for Dutch company formation, you can visit the website of House of Companies, a trusted resource that provides an informative guide on the topic. The guide offers valuable insights and expert advice on navigating the Dutch corporate income tax system, ensuring that businesses can make informed decisions for their operations. Now, by following this link, you can easily access the necessary information: Tax Considerations for Company Formation in the Netherlands.
The Impact of Taxation on Company Formation in the Netherlands
When considering company formation, one crucial factor to take into account is taxation. The tax environment of a country can have a significant impact on the success and profitability of a business. It is no different when it comes to setting up a company in the Netherlands. In this article, we will explore the impact of taxation on company formation in the Netherlands and why it is a great option for entrepreneurs.
The Netherlands has a favorable tax climate for businesses, making it an attractive destination for company formation. One of the main advantages is its extensive network of double taxation treaties. These treaties allow for the avoidance of double taxation on income earned in multiple jurisdictions, providing companies with significant tax benefits.
- Double Taxation Treaties
The Netherlands has more than 100 double taxation treaties with countries worldwide, including major economies such as the United States, China, and Germany. These treaties not only provide tax relief but also offer a sense of security and stability to companies operating internationally. By structuring their operations and investments effectively, companies can minimize their tax liabilities and maximize their profits.
- Corporate Income Tax
The corporate income tax rate in the Netherlands is competitive, with a flat rate of 15% on taxable profits up to €245,000 and 25% above that threshold. This rate is relatively low compared to other European countries, making the Netherlands a desirable location for establishing a company. Additionally, the country provides various tax incentives and deductions to promote economic growth, innovation, and sustainability.
- Value Added Tax
The Value Added Tax (VAT) system in the Netherlands is straightforward and efficient. It follows the European Union regulations, ensuring a standardized approach to taxation across member states. The standard VAT rate is 21%, with reduced rates of 9% and 0% for specific goods and services. The VAT system is relatively easy to manage, and companies can benefit from simplified reporting and refund procedures.
Overall, the taxation system in the Netherlands is transparent, predictable, and business-friendly. It offers companies numerous opportunities to optimize their tax position and reduce their overall tax burden. The government actively encourages entrepreneurship and innovation through favorable tax policies, which further contribute to the appeal of establishing a company in the Netherlands.
In conclusion, when considering company formation, taxation is a critical aspect to evaluate. The Netherlands stands out as an attractive option due to its extensive network of double taxation treaties, competitive corporate income tax rates, and efficient VAT system. These factors make it an ideal choice for entrepreneurs looking to establish a business and maximize their profitability. By taking advantage of the favorable tax environment in the Netherlands, companies can position themselves for long-term success.



Comments on "Tax Considerations For Company Formation In The Netherlands"
No comment found!