Understanding Tax Implications when Forming a Company in the Netherlands
When considering forming a company in the Netherlands, it is essential to understand the tax implications associated with this decision. The Netherlands offers attractive opportunities for businesses due to its favorable tax system and strategic location within Europe. In this article, we will discuss the key tax considerations to keep in mind when establishing a company in the Netherlands.
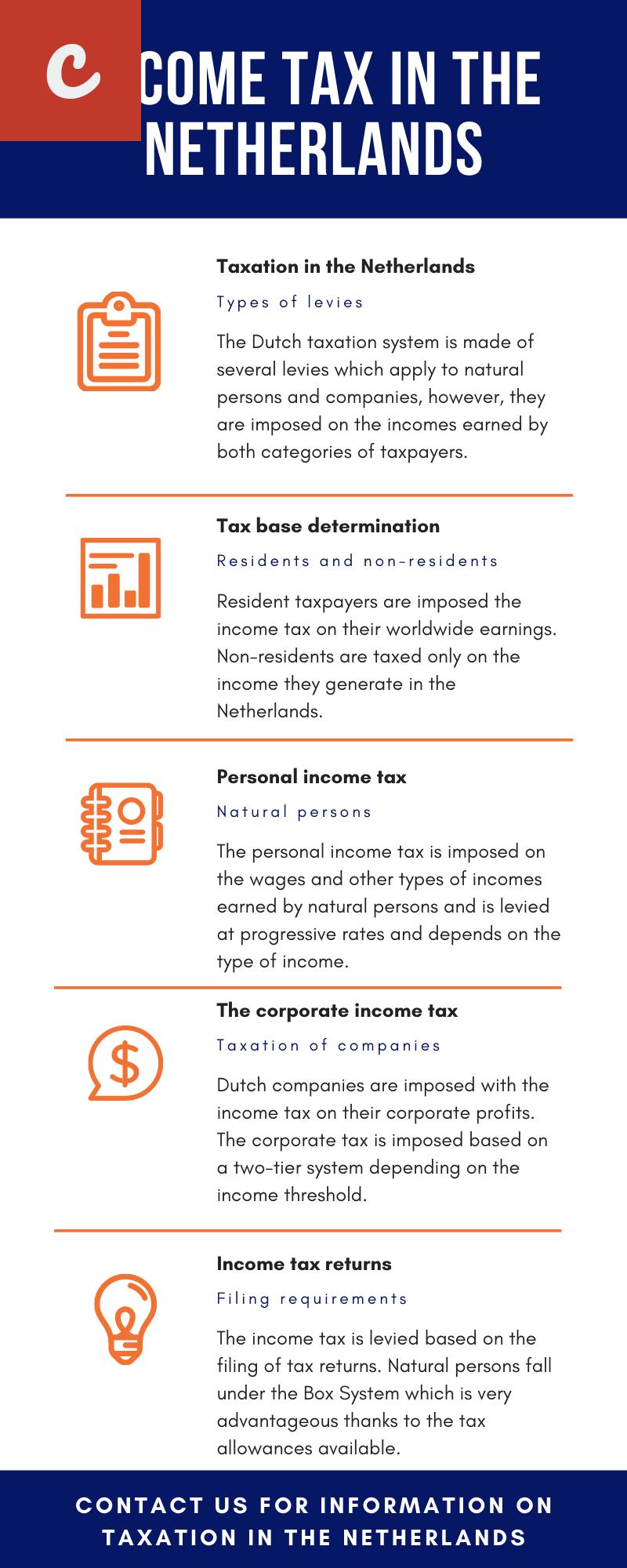
Netherlands Corporate Tax
The Netherlands has a competitive corporate tax rate, which is currently set at 25%. This rate applies to taxable profits exceeding €200,000. For companies with profits up to this threshold, a reduced corporate tax rate of 20% is applicable. It is important to note that the corporate tax rate is scheduled to decrease gradually to 21.7% by 2021.
Value Added Tax (VAT)
The Value Added Tax (VAT) system in the Netherlands is similar to that of other European Union (EU) countries. All businesses in the Netherlands are required to charge VAT on their sales and services unless they fall under specific exceptions. The standard VAT rate in the Netherlands is 21%, with reduced rates of 9% and even 0% applying to certain goods and services. Registering for VAT with the Dutch tax authorities is mandatory for companies exceeding a certain threshold in turnover.
- Withholding Taxes
- Employee Income Tax and Social Security Contributions
When it comes to withholding taxes, the Netherlands has an extensive tax treaty network, which helps to reduce or eliminate taxes on certain types of income, such as dividends, interest, and royalties. This is particularly beneficial for foreign investors and companies operating in the Netherlands.
Employee income tax and social security contributions are crucial aspects of running a business in the Netherlands. Employers are required to withhold income tax from their employees' salaries and make contributions towards the social security system. The tax rates for employees are progressive, with higher earners subject to higher tax rates.
Dutch Tax Residence and Permanent Establishment
Another crucial consideration is determining the tax residence status and potential permanent establishment of your company in the Netherlands. A company is considered a tax resident in the Netherlands if its legal seat or place of effective management is located in the country. On the other hand, a permanent establishment is established if a foreign company has a fixed place of business in the Netherlands.
Conclusion
Forming a company in the Netherlands requires careful consideration of the tax implications involved. The Dutch tax system offers several advantages, including a competitive corporate tax rate, extensive tax treaty network, and favorable VAT system. It is advisable to seek professional advice from a tax expert or consultant to ensure compliance with all tax regulations and to optimize your tax position in the Netherlands.
Main Title: Key Tax Factors to Consider for Company Formation in the Netherlands
When it comes to setting up a company in the Netherlands, there are several tax factors that entrepreneurs need to consider. The Dutch tax system is known to be business-friendly, with various incentives and advantages for companies. However, it is essential to understand and plan for the tax implications of starting a business in the Netherlands to ensure compliance and optimize tax savings. This article explores some key tax factors that entrepreneurs should keep in mind when forming a company in the Netherlands.
- List item 1: Corporate Income Tax: Corporate Income Tax (CIT) is levied on the annual profit of companies operating in the Netherlands. The current CIT rate is 25%, which is comparatively low compared to other European countries. However, it is important to note that small businesses may be eligible for lower tax rates. Businesses that qualify as startups can benefit from a reduced 15% CIT rate for the first profits earned.
- List item 2: Value Added Tax: Value Added Tax (VAT) is a consumption tax applied to most goods and services in the Netherlands. The standard VAT rate in the Netherlands is 21%. However, there are reduced VAT rates of 9% and 0% for certain goods and services. Entrepreneurs should determine if their business activities fall under the scope of VAT and understand the requirements for VAT registration and compliance.
Paragraph 3: Tax Incentives: The Dutch tax system offers various incentives and deductions for businesses. For example, the Innovation Box allows companies to benefit from a reduced CIT rate of 9% on profits derived from eligible innovations. This incentive aims to encourage research and development activities in the Netherlands. Furthermore, the Dutch government provides tax incentives for investments, such as the Investment Allowance and the Energy Investment Allowance, which can reduce the taxable income of businesses.
As with any tax system, compliance with tax regulations is crucial. Entrepreneurs should ensure they have a good understanding of their tax obligations and deadlines to avoid any penalties or non-compliance issues. It is advisable to seek professional advice from tax experts or consult the Dutch Tax and Customs Administration (Belastingdienst) for specific tax-related queries.
In conclusion, entrepreneurs planning to set up a company in the Netherlands should carefully consider the key tax factors discussed in this article. Understanding and planning for corporate income tax, value-added tax, and available tax incentives can contribute to the success and profitability of businesses in the Netherlands. By staying informed and compliant with tax regulations, entrepreneurs can maximize their tax savings and establish a solid foundation for their company formation in the Netherlands.
Navigating Tax Regulations for Setting up a Business in the Netherlands
Setting up a business in the Netherlands can be an exciting and profitable venture. The country offers a favorable business climate, a well-developed infrastructure, and a highly educated workforce. However, before you embark on this journey, it is important to understand the tax regulations in the country.
The first step in setting up a business in the Netherlands is to decide on the legal structure of your company. You can choose between a sole proprietorship, a partnership, or a limited liability company (LLC). Each type of legal structure has different tax implications, so it is important to carefully consider your options.
- Sole Proprietorship: A sole proprietorship is the easiest and most straightforward legal structure to set up. As a sole proprietor, you are personally liable for all debts and liabilities of the business. From a tax perspective, your profits are taxed as personal income.
- Partnership: A partnership is suitable for businesses with multiple owners. In this legal structure, each partner is personally liable for the business's debts and liabilities. The partnership itself is not taxed; instead, each partner is taxed individually on their share of the profits.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): An LLC is a separate legal entity from its owners. This means that the owners, known as shareholders, have limited liability for the company's debts and liabilities. From a tax perspective, an LLC is subject to corporate income tax on its profits. Shareholders are then taxed individually on any dividends they receive from the company.
Once you have determined the legal structure of your company, you need to register with the Dutch Chamber of Commerce (KvK). This registration is mandatory for all businesses operating in the Netherlands. You will receive a unique company registration number (KvK number) that you will need for various administrative and tax purposes.
As an entrepreneur in the Netherlands, you will be responsible for several types of taxes. These include:
- Income Tax: As a business owner, you will be subject to income tax on the profits you generate. The income tax rates in the Netherlands are progressive, meaning that they increase as your income rises. It is important to keep accurate records of your income and expenses to calculate your taxable profit correctly.
- Value Added Tax (VAT): If your annual turnover exceeds a certain threshold, currently set at €20,000, you will need to register for VAT. VAT is a consumption tax that is charged on most goods and services in the Netherlands. As a registered VAT taxpayer, you will need to charge VAT on your sales and remit the collected VAT to the tax authorities.
- Corporate Income Tax (CIT): If your business is structured as an LLC, you will be subject to corporate income tax. The standard corporate income tax rate in the Netherlands is 25%. However, there are certain deductions and incentives available that can reduce your taxable profit and lower your tax liability.
It is recommended to seek professional advice when setting up a business in the Netherlands to ensure compliance with tax regulations and to optimize your tax position. An experienced tax advisor or accountant can guide you through the process and help you navigate the complexities of the Dutch tax system.
In conclusion, understanding and navigating the tax regulations for setting up a business in the Netherlands is crucial for success. By carefully considering the legal structure of your company and complying with the relevant tax obligations, you can ensure a smooth and profitable business venture in this thriving European country.

Tax Planning Tips for Forming a Company in the Netherlands
If you're considering forming a company in the Netherlands, it's crucial to understand the tax implications and plan accordingly. The Netherlands offers a favorable tax climate for businesses, but knowing how to navigate the tax system can help you maximize your company's profits and minimize tax liabilities. Here are some tax planning tips to consider when forming a company in the Netherlands.
1. Choose the right legal entity
When forming a company in the Netherlands, one of the most important decisions you need to make is choosing the right legal entity. The most common options are a BV (Besloten Vennootschap) or NV (Naamloze Vennootschap). Both entities offer various benefits, such as limited liability protection and the ability to attract investors. However, the tax implications differ. Consult with a tax advisor to determine which entity suits your business goals and has the most favorable tax treatment.
2. Utilize the Dutch participation exemption
The Dutch participation exemption is a tax provision that exempts dividend income and capital gains received from participating interests in subsidiaries from corporate income tax. This means that if a Dutch company holds at least 5% of the nominal paid-up share capital of a subsidiary, the profits or gains derived from that subsidiary are exempt from tax in the Netherlands. Utilizing this exemption can help you reduce your overall tax burden.
3. Take advantage of tax treaties
The Netherlands has an extensive network of tax treaties with more than 100 countries, including many major economies. These treaties aim to prevent double taxation and provide tax relief for businesses operating internationally. By leveraging the tax treaties, you can potentially reduce or eliminate the tax liability on income generated in those countries.
- 4. Benefit from the innovation box
- 5. Optimize your company's transfer pricing
Furthermore, the Netherlands offers an innovation box, which provides a reduced corporate income tax rate of 9% on profits derived from qualifying intellectual property rights. If your company develops innovative products, services, or processes, taking advantage of the innovation box can significantly reduce your tax burden.
Another crucial aspect of tax planning is optimizing your company's transfer pricing. Transfer pricing refers to the setting of prices for goods, services, or intellectual property traded within multinational companies. By ensuring that your company's transactions with related entities are conducted at arm's length and comply with transfer pricing regulations, you can minimize the risk of disputes with tax authorities and ensure that profits are allocated appropriately.
In conclusion, tax planning is essential when forming a company in the Netherlands. Choosing the right legal entity, utilizing tax exemptions, leveraging tax treaties, benefiting from the innovation box, and optimizing transfer pricing can help you navigate the Dutch tax system effectively and maximize your company's profitability. Consulting with a tax advisor is highly recommended to ensure compliance with the complex tax regulations and to develop a tailored tax plan for your business.
Tax Considerations for Company Formation in the Netherlands are crucial for businesses planning to establish their presence in the country. One key aspect to understand is the Dutch corporate income tax, which imposes certain obligations on companies operating within its jurisdiction. When setting up a business in the Netherlands, it is essential to familiarize yourself with the tax requirements and regulations to ensure compliance. To gain a comprehensive understanding of Dutch company taxes, it is advisable to consult reputable sources such as the House of Companies website, which provides valuable insights into the tax considerations surrounding company formation in the Netherlands Tax Considerations for Company Formation in the Netherlands.
Important Tax Considerations for Company Formation in the Netherlands
When considering company formation, it is crucial to take into account the tax implications of doing business in a specific country. In this article, we will explore some important tax considerations for company formation in the Netherlands.
The Netherlands has a favorable tax climate for businesses, making it an attractive destination for company formation. However, to fully benefit from the Dutch tax system, it is essential to understand and comply with the local tax regulations.
- Corporate Income Tax: Companies in the Netherlands are subject to corporate income tax on their worldwide profits. The standard corporate income tax rate is 25% on taxable profits up to €200,000 and 21.7% on taxable profits exceeding this threshold. Small or medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may be eligible for reduced tax rates.
- Value Added Tax (VAT): VAT is a consumption tax applied to the sale of goods and services. In the Netherlands, the standard VAT rate is 21%. However, certain goods and services may qualify for reduced rates, such as the 9% rate applicable to food, books, and healthcare services.
Another key tax consideration for company formation in the Netherlands is the country's extensive network of tax treaties. The Netherlands has signed tax treaties with numerous countries, aiming to avoid double taxation and provide favorable tax arrangements for businesses carrying out cross-border activities. These tax treaties can help minimize tax liabilities and provide certainty to companies operating internationally.
Additionally, the Netherlands offers a range of tax incentives to attract investment and promote innovation. For instance, there are various tax deductions available for research and development (R&D) activities, innovation projects, and investments in environmentally friendly assets.
As part of company formation in the Netherlands, it is also important to consider the Dutch payroll tax system. If you plan to hire employees in the country, you will need to register with the Dutch Tax and Customs Administration and comply with payroll tax regulations. These regulations include withholding payroll taxes from employees' salaries and reporting them to the tax authorities.
In conclusion, when considering company formation in the Netherlands, it is crucial to keep in mind the various tax considerations. Understanding the corporate income tax rates, VAT regulations, tax treaties, and available tax incentives will help you make informed decisions and optimize your tax position. Consulting with a tax professional can provide valuable guidance and ensure compliance with all relevant tax regulations.



Comments on "Tax Considerations For Company Formation In The Netherlands"
No comment found!