Understanding Taxes and Financial Aspects of Setting Up a Company in the Netherlands
Setting up a company in the Netherlands can be an exciting and lucrative endeavor. With its strong economy, favorable business climate, and strategic location in Europe, the Netherlands has become an attractive destination for entrepreneurs and investors alike. However, it is important to understand the taxes and financial aspects associated with starting and running a business in this country.
Taxes play a crucial role in the financial landscape of any business, and the Netherlands is no exception. The Dutch tax system is known for its transparency and efficiency, but it can also be quite complex. It is advisable to have a good understanding of the different types of taxes that apply to businesses in the Netherlands.
One of the most important taxes to be aware of is the corporate income tax (CIT). This tax is levied on the profits generated by a company in the Netherlands. The standard CIT rate in the Netherlands is currently 25%. However, there are certain exceptions and deductions that can apply, depending on the size and nature of the business.
In addition to the CIT, businesses in the Netherlands are also subject to value-added tax (VAT), also known as sales tax. The standard VAT rate in the Netherlands is 21%, with reduced rates of 9% and 0% applying to certain goods and services. Companies are required to register for VAT and file regular VAT returns with the Dutch tax authorities.
Another important tax aspect to consider is employee taxes. If you plan to hire employees in the Netherlands, you will need to be aware of the various social security contributions, payroll taxes, and income tax withholding requirements. These taxes can have a significant impact on your overall labor costs.
- CIT (Corporate Income Tax)
- VAT (Value-Added Tax)
- Employee taxes
Aside from taxes, there are other financial aspects to consider when setting up a company in the Netherlands. One of these is the legal structure of your business. The most common legal entities in the Netherlands are private limited liability companies (BV) and sole proprietorships. Each structure has its pros and cons, so it is important to seek professional advice to determine the best fit for your business.
Furthermore, you will need to consider the banking and accounting requirements in the Netherlands. Opening a business bank account is essential for managing your company's finances effectively. Additionally, it is important to maintain accurate and up-to-date financial records in accordance with Dutch accounting regulations.
Finally, one should not overlook the importance of business insurance. In the Netherlands, certain types of insurance, such as liability insurance and disability insurance, are mandatory for businesses. It is important to evaluate your specific insurance needs to protect your company from potential risks and liabilities.
In conclusion, while setting up a company in the Netherlands offers numerous benefits, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of the taxes and financial aspects involved. Being aware of the various taxes, legal structures, banking requirements, and insurance needs will enable you to navigate the Dutch business landscape successfully.
Navigating Tax Laws and Financial Considerations for Dutch Company Formation
Starting a new business can be an exciting venture, but it's important to understand the legal and financial aspects involved. For those looking to establish a company in the Netherlands, it's crucial to navigate the country's tax laws and consider financial implications. This article will provide an overview of the key factors to consider when forming a Dutch company.
One of the first steps in setting up a company in the Netherlands is choosing the right legal structure. The most common types of legal entities are a private limited liability company (BV) or a public limited company (NV). Each structure has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of liability, governance, and tax requirements.
- List item 1: A BV offers limited liability protection for shareholders, meaning their personal assets are generally not at risk in case of company debts or legal issues. It also allows for flexible profit distribution and easier transfer of ownership.
- List item 2: An NV, on the other hand, is more suitable for larger-scale businesses seeking public financing or planning to go public in the future. However, it has stricter governance requirements and may involve higher costs.
Once the legal structure is determined, understanding the Dutch tax system is crucial. The Netherlands has an attractive tax regime for businesses, with various tax incentives and favorable regulations. One of the key benefits is the participation exemption, which exempts qualifying dividend and capital gains from subsidiaries. This makes the Netherlands an attractive location for holding companies.
Foreign investors planning to establish a Dutch company should also be aware of tax treaties that the Netherlands has with other countries. These treaties aim to avoid double taxation and provide mechanisms for businesses to claim tax credits or exemptions.
Value-added tax (VAT) is another important consideration for businesses in the Netherlands. Generally, businesses are required to register for VAT if their annual turnover exceeds a certain threshold. VAT rates in the Netherlands vary depending on the type of goods or services provided.
Furthermore, it is important to consider the financial implications of establishing a company in the Netherlands. Businesses must create a financial plan outlining their projected revenues, expenses, and funding sources. They should also consider the costs of complying with financial reporting and auditing requirements.
In conclusion, starting a Dutch company involves careful navigation of tax laws and financial considerations. Choosing the right legal structure, understanding the tax regime and incentives, and considering VAT obligations are crucial steps. It is also vital to develop a sound financial plan and be aware of financial reporting requirements. Seeking professional advice from tax and legal experts can help ensure compliance and optimize financial outcomes.
Essential Taxation and Financial Factors to Consider when Establishing a Company in the Netherlands
When it comes to establishing a company in the Netherlands, there are several essential taxation and financial factors that you need to consider. The Netherlands is known for its favorable tax climate and business-friendly policies, making it an attractive destination for entrepreneurs and investors alike. To ensure that your company is set up for success, here are some key considerations:
Taxation:
One of the main advantages of establishing a company in the Netherlands is its favorable tax system. The country offers several tax incentives and benefits that can help your business thrive. For instance, the corporate tax rate is relatively low compared to other European countries, currently standing at 15% for profits up to €200,000 and 25% for profits above that threshold. Additionally, the Netherlands has an extensive network of double taxation treaties, which can help you avoid being taxed twice on the same income.
Another important aspect to consider is the Value Added Tax (VAT) system. The Netherlands has a standard VAT rate of 21%, with reduced rates of 9% and 0% for specific goods and services. Familiarize yourself with the Dutch VAT regulations to ensure compliance with the local tax authorities.
Finally, it's important to understand the implications of transfer pricing regulations. The Netherlands has strict rules in place to prevent tax evasion and ensure fair transactions between related parties. Make sure your company follows the relevant guidelines to avoid any unwanted attention from the tax authorities.
Financial Regulations:
Apart from taxation, there are other financial regulations you should be aware of when setting up a company in the Netherlands. For instance, the Dutch government requires all companies to file annual financial statements with the Chamber of Commerce. These statements need to comply with the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or the Dutch Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
Additionally, the Netherlands has a well-established banking sector with numerous financial institutions. It's advisable to open a local bank account to facilitate day-to-day financial transactions and ensure compliance with the Dutch banking regulations.
- Choose a reliable and experienced tax advisor or accountant to assist you with your financial matters and ensure compliance with Dutch regulations.
- Consider the potential benefits of structuring your company as a Dutch holding company to take advantage of the favorable tax treaties.
In conclusion, establishing a company in the Netherlands offers numerous advantages in terms of taxation and financial regulations. By understanding and planning for these essential factors, you can set up your business for success and take full advantage of the favorable business climate in the country.
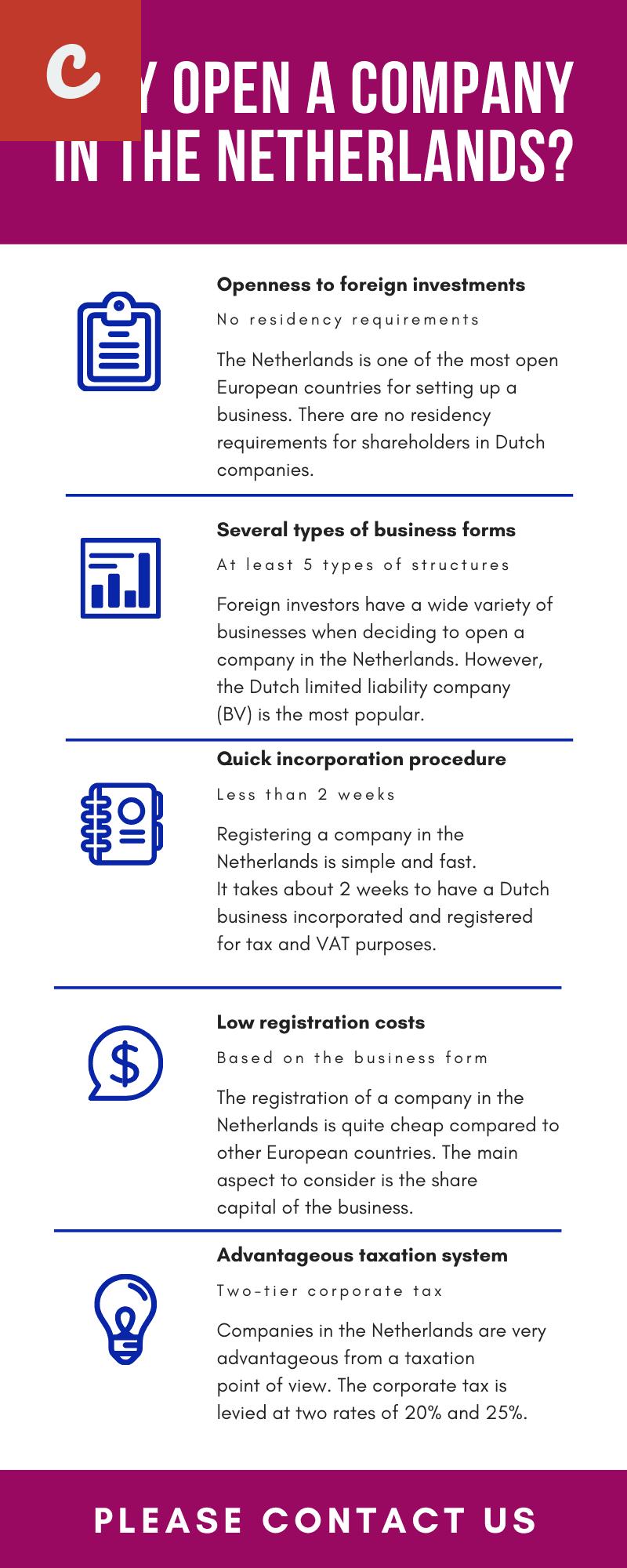
A Guide to Taxation and Financial Considerations for Starting a Business in the Netherlands
Starting a business is an exciting venture, but it also requires careful planning and consideration of various aspects, including taxation and financial matters. If you are considering starting a business in the Netherlands, it is important to understand the tax landscape and other financial considerations to ensure a smooth and successful launch. This guide will provide you with the essential information you need to know.
One of the first things to consider when starting a business in the Netherlands is the tax regime. The Dutch tax system is known for its complexity, so seeking professional advice from a tax specialist or accountant is highly recommended. That being said, here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Corporate Income Tax: Any company registered in the Netherlands is subject to corporate income tax on its worldwide income. The standard corporate income tax rate is currently set at 25%. However, there are lower rates for profits up to a certain threshold, called the "Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SME) rate".
- Value Added Tax (VAT): VAT is a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and services. The standard VAT rate in the Netherlands is currently 21%, but reduced rates of 9% and 0% apply to certain goods and services. As a business owner, you will have various VAT obligations that need to be accounted for, such as registration, invoicing, and reporting.
Another important aspect to consider is the legal form of your business. The most common legal forms in the Netherlands are sole proprietorship, partnership, and limited liability company. Each has its own implications in terms of liability, tax obligations, and reporting requirements. Again, consulting with a legal expert is advisable to determine the most suitable legal form for your business.
Registration is a crucial step when starting a business in the Netherlands. You will need to register your business with the Dutch Chamber of Commerce (Kamer van Koophandel) and obtain a unique identification number (KvK number). This number will be required for various purposes, including tax administration, hiring employees, and opening a business bank account.
Furthermore, understanding the employee-related taxes and contributions is essential if you plan on hiring employees in the Netherlands. You will be responsible for deducting and remitting income tax, social security contributions, and pension premiums from your employees' salaries. Ensuring compliance with employment laws and regulations is essential to avoid any legal issues.
In addition to taxes, there are other financial considerations you should keep in mind when starting a business in the Netherlands. These include creating a comprehensive business plan, securing financing, and setting up an efficient accounting system to keep track of your income and expenses. Hiring a skilled bookkeeper or accountant can greatly assist you in managing your finances effectively.
In conclusion, starting a business in the Netherlands involves several taxation and financial considerations. It is crucial to familiarize yourself with the Dutch tax system, seek professional advice, and understand the legal and financial implications of your chosen business form. By doing so, you can ensure a solid financial footing and set yourself up for success in the Dutch business landscape.
Key Tax and Financial Considerations for Company Formation in the Netherlands
Starting a company in the Netherlands can be an exciting endeavor with many opportunities for growth and success. However, before embarking on this journey, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of the key tax and financial considerations involved in the company formation process. This article will outline some essential points to keep in mind.
First and foremost, it is essential to understand the different types of entities that can be formed in the Netherlands. The most common forms are a private limited liability company (BV) and a sole proprietorship (eenmanszaak). While a BV provides limited liability protection, an eenmanszaak is simpler to establish but does not offer the same level of protection.
Tax implications play a vital role in deciding the type of entity to form. A BV is subject to corporate income tax on its profits, while an eenmanszaak is subject to income tax. The corporate income tax rate in the Netherlands is typically lower than the personal income tax rate, making a BV an attractive option for many entrepreneurs.
- Advantages of a BV: A BV offers limited liability protection, separate legal entity status, and the ability to attract investors by issuing shares.
- Advantages of an eenmanszaak: An eenmanszaak is simpler to form, has lower administrative costs, and allows for more flexibility in terms of business management.
Another crucial consideration is the Value Added Tax (VAT). In the Netherlands, businesses with an annual turnover exceeding a certain threshold must register for VAT. VAT rates vary depending on the type of goods or services provided.
Additionally, it is important to be aware of the Dutch tax regime. The Netherlands has a unique tax system that includes various incentives for businesses, such as the participation exemption and the innovation box. These incentives aim to attract foreign direct investment and foster innovation.
When establishing a company in the Netherlands, it is crucial to have a proper accounting and bookkeeping system in place. This includes maintaining accurate financial records, staying up to date with tax regulations, and filing annual financial statements with the Chamber of Commerce.
Lastly, it is highly recommended to seek professional advice from a tax advisor or accountant experienced in Dutch tax law. They can provide guidance on the optimal corporate structure, tax planning opportunities, and help ensure compliance with Dutch tax regulations.
In conclusion, setting up a company in the Netherlands offers numerous advantages, but it's important to be aware of the key tax and financial considerations. Understanding the tax implications, VAT requirements, and the Dutch tax regime is crucial for making informed decisions. By seeking expert advice and staying compliant with the relevant regulations, you can lay a strong foundation for a successful business in the Netherlands.




Comments on "Taxation And Financial Considerations For Company Formation In The Netherlands"
No comment found!