Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Business Structure in the Netherlands
When starting a business in the Netherlands, one of the most important decisions you'll have to make is choosing the right business structure. The business structure you choose will have legal and financial implications, so it's essential to understand the key factors that should influence your decision.
Types of Business Structures in the Netherlands
Before diving into the key factors, let's first look at the different types of business structures you can opt for in the Netherlands:
- Sole Proprietorship: As the name suggests, this is a business owned by a single person.
- Partnership: A partnership is a collaboration between two or more people who share the profits and losses of the business.
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): An LLC is a separate legal entity that provides limited liability to its owners.
- Public Limited Company (PLC): A PLC is a company whose shares are publicly traded on the stock exchange.
Key Factors to Consider
Now, let's explore the key factors you should consider when choosing a business structure in the Netherlands:
1. Liability Protection: The level of liability protection provided by a business structure is crucial, especially if you're concerned about personal assets being at risk. For instance, forming an LLC or PLC can offer limited liability protection, shielding personal assets from business debts.
2. Tax Implications: Another crucial factor to consider is the tax implications of different business structures. Depending on the structure you choose, you may have different tax obligations. Research the tax rates and benefits associated with each business structure to make an informed decision.
3. Corporate Governance: If you plan to have a complex management structure with multiple shareholders and a board of directors, a PLC may be the best option. Sole proprietorships and partnerships are usually simpler to manage and have less formal requirements.
4. Funding Options: Consider the potential growth of your business and the funding options available with each business structure. For example, if you plan to attract investors or issue shares, a PLC may be more suitable. Sole proprietorships and partnerships, on the other hand, rely heavily on personal funds.
5. Flexibility: Think about the flexibility you require in terms of decision-making, profit distribution, and potential business changes. Certain business structures, such as partnerships, offer more flexibility compared to others.
6. Longevity: Consider the long-term goals of your business. Different business structures have different implications for continuity and succession planning. For instance, a sole proprietorship ends with the death of the owner, while an LLC can continue its operations with new owners.
Conclusion
In conclusion, choosing the right business structure in the Netherlands is a significant decision that will impact your legal, financial, and operational activities. Evaluate the key factors discussed, seek professional advice, and carefully consider your specific business needs before making a final decision. By doing so, you'll be able to establish a strong foundation for your business and pave the way for future success.
Understanding the Different Business Structures in the Netherlands: A Guide
Starting a business in the Netherlands can be an exciting endeavor, but it is important to understand the different business structures available in the country. Choosing the right structure is crucial as it will determine legal liability, tax obligations, and operational flexibility. This guide will explain the different business structures in the Netherlands to help you make an informed decision.
1. Sole Proprietorship: A sole proprietorship is the simplest and most common form of business structure in the Netherlands. It is suitable for individuals running small businesses with no employees. As a sole proprietor, you have complete control over your business and are personally liable for any debts or legal issues.
2. Partnership: A partnership is formed when two or more individuals come together to start a business. There are two types of partnerships in the Netherlands: general partnership (VOF) and limited partnership (CV). In a general partnership, all partners are equally liable for the debts and obligations of the business. In a limited partnership, there are general partners and limited partners. General partners have unlimited liability, while limited partners have limited liability.
- General partnership (VOF): All partners share equal responsibility and liability.
- Limited partnership (CV): Consists of general partners (unlimited liability) and limited partners (limited liability).
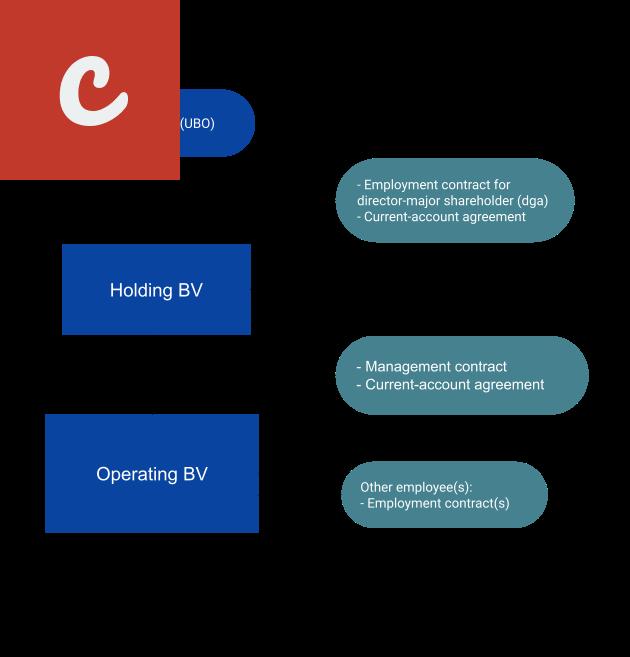
3. Private Limited Company (BV): A private limited company, also known as a BV (Besloten Vennootschap), is an independent legal entity separate from its shareholders. This structure provides limited liability, meaning that shareholders are only liable for the capital they have invested. A BV requires minimum share capital and is subject to certain administrative and reporting requirements.
4. Public Limited Company (NV): A public limited company, also known as a NV (Naamloze Vennootschap), is suitable for larger businesses planning to go public. It requires a higher minimum share capital and is subject to more stringent reporting and disclosure requirements. Shareholders have limited liability.
5. Cooperative (Coöperatie): A cooperative is a business structure where individuals or companies come together for a common purpose. Each member of the cooperative has equal voting rights and can benefit from shared resources and profits. A cooperative can be formed by companies or individuals from various industries.
When choosing a business structure in the Netherlands, it is important to consider factors such as liability, tax implications, and governance. Consulting with a legal or tax advisor can help you fully understand the implications of each structure and make the best decision for your business.
In conclusion, understanding the different business structures in the Netherlands is essential for anyone looking to start a business in the country. Each structure has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to carefully weigh your options before making a decision. By choosing the right structure, you can ensure the success and growth of your business in the Netherlands.
Choosing the Best Business Structure for Your Dutch Venture: Tips and Advice
Starting a business in the Netherlands requires careful consideration and research. One crucial aspect of setting up a successful venture is choosing the right business structure. The business structure you select will determine the legal and financial aspects of your company, so it's vital to make an informed decision.
Here are some tips and advice to help you choose the best business structure for your Dutch venture:
- Sole Proprietorship: This is the simplest and most common business structure. It's suitable for entrepreneurs who want to operate their business alone and have complete control over decision-making. However, it also means that you'll have unlimited liability for any business debts.
- Partnership: If you plan to start a business with one or more partners, a partnership structure may be a good option. There are two types of partnerships in the Netherlands: general partnership (VOF) and limited partnership (CV). In a general partnership, partners share responsibilities and have unlimited liability. In a limited partnership, there are two types of partners: general partners with unlimited liability and limited partners who have limited liability.
- Private Limited Company (BV): A BV is a separate legal entity and provides limited liability for its shareholders. This structure is ideal for medium to large-sized businesses that aim to grow and attract external investors. A BV also offers more flexibility in terms of ownership and transfer of shares.
- Public Limited Company (NV): An NV is similar to a BV but allows for the public trading of shares. This structure is suitable for larger companies planning to go public and raise funds from the stock market.
It's essential to consider factors like liability, control, taxation, and future growth plans while selecting the best business structure for your Dutch venture. Consulting with a business lawyer or tax advisor can help you navigate the legal and financial aspects involved.
Choosing the right business structure will have long-term implications for your Dutch venture. It will impact your legal obligations, taxation, and ability to attract investors. Therefore, it's crucial to conduct thorough research and seek professional advice before making a decision.
Main Title
When starting a business in the Netherlands, one of the most crucial decisions you need to make is choosing the right business structure. The business structure you choose will determine various aspects of your business, including taxation, legal liability, and management. Therefore, it is important to carefully consider all the options available to you before making a decision. In this article, we will discuss some important considerations to keep in mind when selecting the right business structure in the Netherlands.
One of the first things you need to determine is whether you want to establish a sole proprietorship or a legal entity. Sole proprietorship is a popular choice for small businesses as it is easy to set up and maintain. However, it also means that you are personally liable for any debts or legal issues that may arise. On the other hand, forming a legal entity such as a limited liability company (LLC) or a corporation can offer more protection for your personal assets.
- List item 1: Taxation is an important consideration when choosing a business structure in the Netherlands. Different structures have different tax implications. For example, sole proprietors are taxed on their personal income, while legal entities are subject to both corporate income tax and dividend tax. It is important to consult with a tax advisor to understand the tax consequences and benefits of each structure.
- List item 2: Another factor to consider is the administrative and reporting requirements. Legal entities are typically subject to more stringent reporting obligations than sole proprietors. You may need to file annual accounts, hold shareholder meetings, and maintain a registered office. This can result in additional administrative costs and time commitments.
It is also important to consider the long-term goals and growth potential of your business. If you plan to seek external funding or take on partners in the future, a legal entity may be more suitable. Legal entities have more flexibility in terms of ownership structure and can easily transfer ownership through the sale of shares. Sole proprietorships, on the other hand, are generally limited to a single owner.
Lastly, it is advisable to seek professional advice when choosing a business structure in the Netherlands. Consulting with a lawyer or a business advisor who is familiar with Dutch business laws and regulations can help you make an informed decision. They can assess your specific situation and guide you towards the most suitable structure for your business.
Conclusion
Selecting the right business structure is an important decision that will impact your business in various ways. Consider factors such as taxation, liability, administrative requirements, and long-term goals when making this decision. Seeking professional advice can help you navigate the complexities of Dutch business laws and ensure that you choose the structure that best aligns with your business objectives.
Choosing the Right Business Structure in the Netherlands
Starting a business in the Netherlands is an exciting venture, but one of the most important decisions you'll need to make is choosing the right business structure. The business structure you choose will have a significant impact on your liability, taxes, and overall flexibility. Here, we will explore the different business structures available in the Netherlands and help you make an informed decision.
1. Sole Proprietorship:
A sole proprietorship is the simplest and most common business structure in the Netherlands. As a sole proprietor, you have complete control over your business and are personally responsible for all liabilities. This structure is suitable for small businesses with low risk. However, it's worth noting that sole proprietors don't have limited liability protection, which means your personal assets are at risk if the business faces any financial or legal troubles.
2. Partnership:
If you plan to start a business with another person, a partnership may be the right choice for you. There are two types of partnerships in the Netherlands: general partnerships (VOF) and limited partnerships (CV). In a general partnership, all partners share equal responsibility for the liabilities and management of the business. In a limited partnership, there is at least one general partner who has unlimited liability and one or more limited partners who are only liable for their capital contribution. Partnerships are a popular choice for businesses in sectors such as professional services or creative industries.
3. Private Limited Company (BV):
A private limited company (BV) is the most commonly used business structure for larger or more complex businesses in the Netherlands. As the name suggests, the liability of the shareholders is limited to their capital contributions. Establishing a BV requires a minimum share capital of €0.01. This structure offers more options for raising capital and is often chosen by entrepreneurs looking to grow their business and attract investors. It also provides more protection for shareholders' personal assets.
- Benefits of a BV:
- - Limited liability protection for shareholders
- - Easier to attract investors and raise capital
- - Separate legal entity from the shareholders
- - Enhanced business credibility and reputation
4. Public Limited Company (NV):
A public limited company (NV) is suitable for businesses with plans of going public and being traded on the stock exchange. Unlike a BV, an NV requires a minimum issued share capital of €45,000. The liability of the shareholders is limited to their capital contributions. An NV is subject to additional regulations and reporting requirements compared to other business structures. This structure is more suitable for larger corporations with substantial capital and a wider shareholder base.
Choosing the right business structure is essential for the long-term success and sustainability of your business. It's important to consult with professionals such as lawyers and accountants who can provide personalized advice based on your specific needs. Take the time to research and consider all your options carefully to make an informed decision that aligns with your business goals and helps you navigate the Dutch business landscape with confidence.



Comments on "Tips For Choosing The Right Business Structure In The Netherlands"
No comment found!